A single network fault may ruin your whole day; if this problem occurs in large-scale industries, you couldn’t expect what it causes. A network problem is a common everyday issue, and I can't sit silently without solving it. In this troubleshoot network connectivity post, we will guide you through some valuable concepts that include troubleshooting network connection, best practices, and the tools used. I know you all are excited about this post, then what are you waiting for? Let’s get started;
Here is our list of the top tools to troubleshoot network connectivity:
- SolarWinds Engineer's Toolset SolarWinds offers a network software and engineer toolset that holds more than 600 tools that have been widely used in troubleshooting network connections.
- Obkio A simple network solution software tool that offers an end-to-end and performance monitoring solution that helps you keep track of the network's health and core business applications.
- Auvik This SaaS package provides network discovery and mapping plus device monitoring with SNMP and traffic tracking with flow protocols. The cloud-based system enables multiple networks to be monitored from one location. Other options include a Wi-Fi monitoring service.
- Ping The ping troubleshoot tool verifies the reachability to the destination host at the remote end by using IP ICMP echo requests.
- Traceroute The traceroute tool sends the ICMP echo requests to step by step in the IP address TTL (time to live) values.
- Protocol Analyser A protocol analyzer is an advanced tool used to identify network issues. This software intercepts and records the data packet flow between the source and destinations.
What do you mean by network connection problem?
Suppose you are experiencing any kind of network connection problem, then you must not reach any resources to perform various operations. The network connectivity enables users to access, gather information, share, and use your organization's resources (or data). In technical terms, you can also define a network connection as establishing communication within the enterprise. So we should consider it a serious issue and try to resolve it using various techniques (we will discuss them in the next section of the post).
What Causes the Network Connectivity Problems
Many significant reasons may cause network connectivity errors in your organization. We would like to list a few of them:
- Large downloads Downloading includes extensive files, software applications, and essential documents (over 100 pages). All these downloaded stuff are stored in your computer’s hard drive using the internet. File transfer or backups consume higher bandwidth; the larger the file size, the higher the bandwidth.
- Latency Is nothing but the time taken by a data packet to reach the specified destination in a network. This performance also gets delayed because of consistency delay or any odd spikes that hinder and affect bandwidth time.
- Packet loss Occurs when a data packet drops during the performance that cannot reach its destination. This is considered a great deal because this problem occurs utterly dependent on how much of the data does not match the final destination.
- Video streaming From the internet uses a high bandwidth, and also video streaming in 7K can consume up to 200 times more bandwidth than audio streaming.
- Large application usage Different applications need different requirements to enable them to work. To use applications, all we need is an internet connection, web development browsers to download the applications, emails, and many more. To function all these applications, we need high bandwidth internet usage.
- Larger file sharing Some application programs require users to share them from the computer-to-computer connection over the network connection (internet). Therefore, they need higher bandwidth because of extensive file downloading and the transfer of extensive files over the internet.
- High CPU usage The central processing unit or CPU is the significant component of any computer that performs primary operations, like receiving and processing instructions for system applications and operating systems, so that you can expect high bandwidth usage over the internet.
- Physical connectivity issues This seems obvious, but some network issues occur because of the hardware devices (RAM, ROM, CD, memory storage) if the storage capacity exceeds the actual storage capacity.
How to Troubleshoot Network Connection?
This section will explain 8 basic steps to resolve any connection issue. Let’s get started:
1. The first and foremost step is to check with your internet connection settings
If you face a network issue, check with your WIFI settings. To do it, follow this navigation:
Go to Settings -> Network & Internet -> select the “Wi-Fi” settings ->then enable the wifi option button as shown in the below diagram:
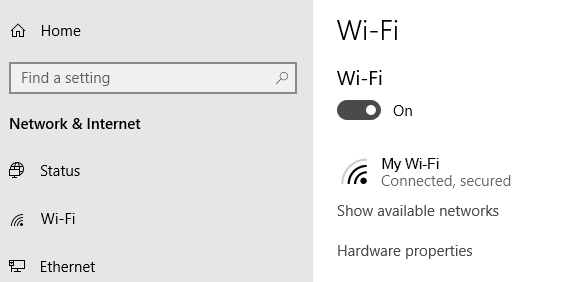
Phones and tablets have the same setting type; just turn on the “Wifi” button and ensure that you have enabled the “ON” button to connect to the network as shown below:
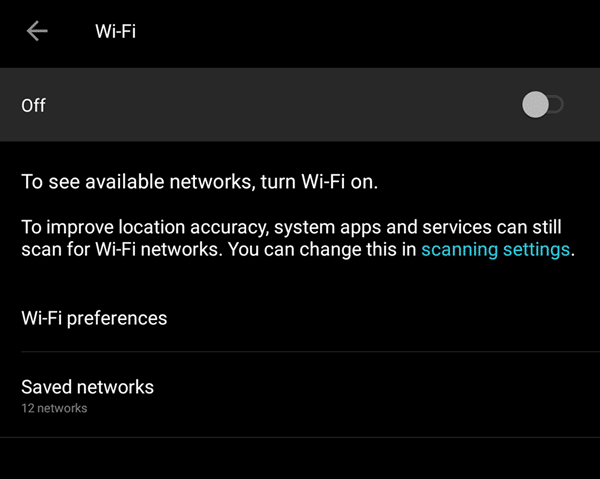
You also check once if you have turned on “Airplane” mode.
2. Check your Access point
Check your WAN (wide area network) and LAN (local area network) connections. If possible, check one of Layman’s ethernet cables because that is always connected to routers.

If you suspect the cables are damaged/ culprit, try to replace them with the new one.
3. Go around obstacles
Sometimes walls, furniture, and other things may cause you to not connect to the internet. By then, have a closer look into the router connection; if you found any type of disconnection, try to re-establish the connection.
Note: We have a myth that moving closer to the router doesn’t solve the issue instead of removing the suspected parts.
4. Restart the router
Sometimes restarting the router may help you solve the network issue. For example, we can say that this might be the real reason you forgot to turn off the router. So restarting the router helps you jolt the router connection into working mode. If that does not work correctly, try to reset the router connection that can be done in the factory setting (if you are okay, then only go for the factory setting option because you might lose data). To configure the router setting by providing an SSID and password.
5. Check with WIFI name password
First, check with your network name (commonly known as SSID) and the network connection password. Suppose, sometimes, if you are trying to establish a connection automatically using a router range, remember that this type of router does not exist for a long time. The below image explains this scenario properly:
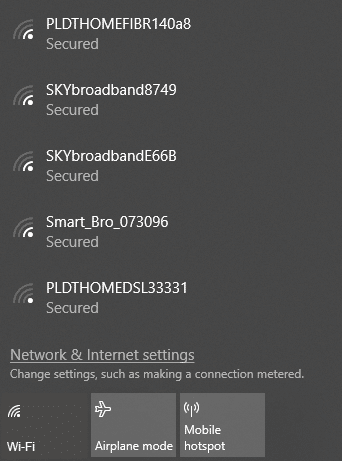
This type of setting could be simple as administrator settings just by updating the password or the SSID.
6. Check the DHCP settings
They usually set routers up as DHCP services and enable users to connect automatically if you turn on the “DHCP services,” so there is no need to mess up with the IP address and manual DNS settings.
If you want to edit your DHCP settings, follow the below navigation:
Go to Windows settings -> select the option Network, and internet -> turn on “WiFi”. Under the WiFi, settings click on the Manage known networks -> then select a network type and click on “properties” as shown below:
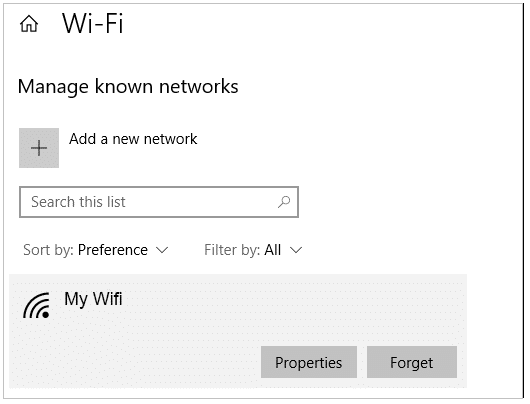
Under the IP setting option -> click the “Edit” option from the drop-down menu -> select the automatic( DHCP) connection.
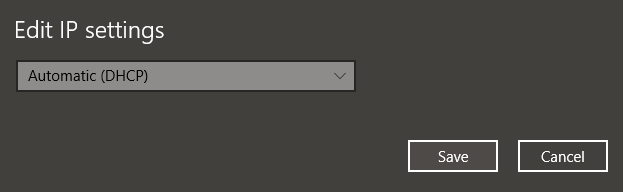
Note: selecting a manual connection will enable users to set their DNS server address and IP address settings manually.
7. Update windows
Your system causes some network problems; if that is the case, you need to fix the network problem. So try updating the windows operations as per the current release version.
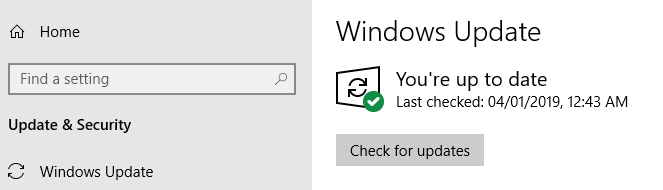
To update the windows, follow this navigation: Go to windows settings -> go to edit and security -> windows update-> click on check for the Updates. If updates are already available, Windows will automatically download and install them.
8. Open windows network diagnosis
Windows consists of a “windows network diagnostic” tool, which helps users troubleshoot the connection issue.
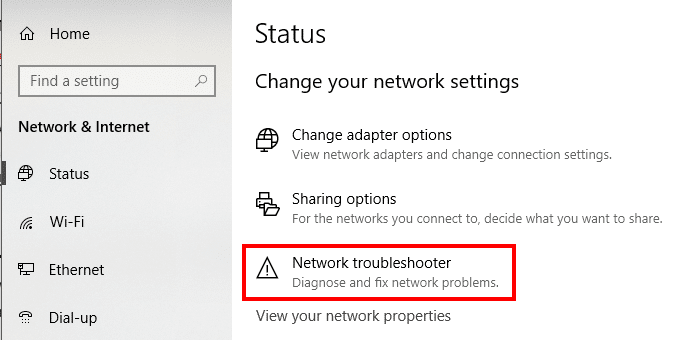
To do this, follow the navigation: Go to the windows settings option-> select the network and internet option -> click the status. Now under the change your network settings -> click the troubleshooter option as shown below:
Windows network diagnostics run a couple of tests to check what is causing the network issue.
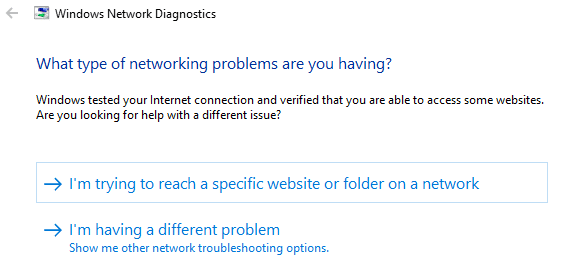
Once done with this step, Windows will let you know the error causing an issue or list a few possible errors that we should resolve.
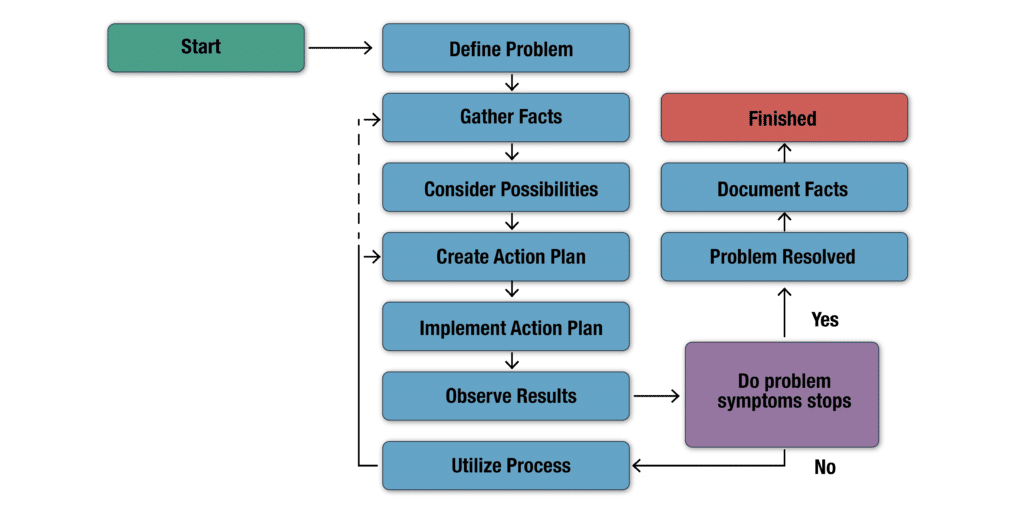
Network Troubleshooting Flowchart
Network troubleshooting is a big headache for us, so we all need an efficient and painless solution and best practices. This section will explain a streamlined process flowchart to explain it better.
The below flowchart is just a roadmap that guides you on how to solve the network issues.
Key Network Troubleshooting Tools
Our methodology for selecting network troubleshooting tools and software
We reviewed the network troubleshooting tools and software market and analyzed the options based on the following criteria:
- An autodiscovery system to log all network devices
- A network topology mapper
- The ability to collect live network devices statuses by using various methods
- A facility to analyze network performance over time
- Graphical interpretation of data, such as charts and graphs
- A free trial period, a demo, or a money-back guarantee for risk-free assessment
- A good price that reflects value for money when compared to the functions offered
Various tools are available on the market to resolve the network connection issue. Here we would like to list out a few tools that will help with this; let’s get started:
1. SolarWinds Engineer's Toolset
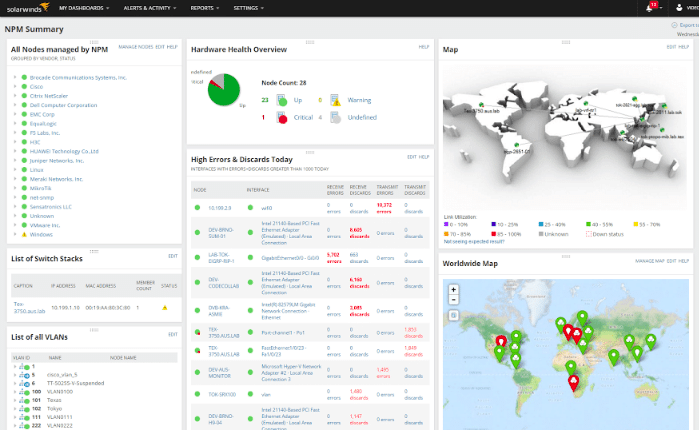
SolarWinds offers a network software and Engineer's Toolset that holds more than 600 tools that have been widely used in troubleshooting network connections. It also provides automated network discovery services such as port scanners, switching off a port mapper, IP network browsers, and many more.
Key Features:
- Extensive Toolkit: Over 60 tools for comprehensive network diagnostics and management.
- Automated Discovery: Facilitates effortless mapping and monitoring of network devices.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Keeps tabs on network performance and alerts proactively.
- IP Management: Features for managing IP addresses and DHCP monitoring efficiently.
- Configuration Tools: Simplifies network device configuration and management.
Why do we recommend it?
The SolarWinds Engineer's Toolset is recommended for its extensive collection of over 60 network management tools, making it a versatile solution for diagnosing and resolving network issues efficiently.
This software also contains powerful diagnostic capabilities, real-time monitoring, alerting, IP address features, DHCP monitoring, log management, and configuration operations.
Who is it recommended for?
This toolset is ideal for network administrators and on-site technicians who require a robust set of tools for detailed network diagnostics, real-time monitoring, and effective network management.
Pros:
- Versatile Tools: Equips sysadmins with a robust suite for network troubleshooting.
- Device Testing: Facilitates easy identification and testing of network devices.
- Functional Verification: Assures network operability across various devices.
- Exportable Diagnostics: Allows for the easy sharing of scan results.
Cons:
- Limited Audience: Primarily designed for sysadmins, less suitable for casual users.
2. Obkio
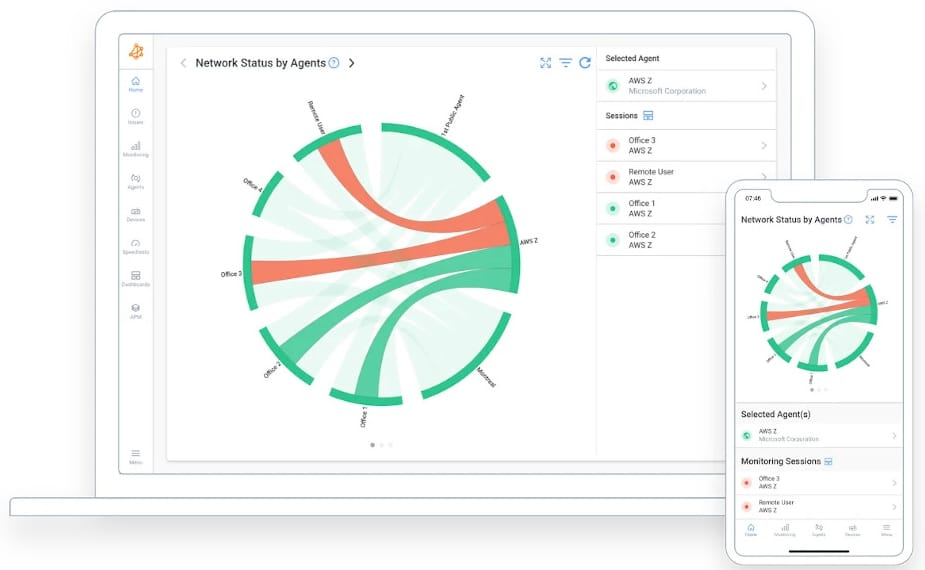
Obkio is a simple network solution software tool that offers an end-to-end and performance monitoring solution that helps you keep track of the network's health and core business applications.
Key Features:
- End-to-End Monitoring: Offers comprehensive insights into network and application performance.
- Alerting Flexibility: Supports various methods for immediate issue notification.
- Multi-Platform: Accessible on both desktop and mobile devices for versatile monitoring.
- Quick Troubleshooting: Identifies and locates sources of network issues efficiently.
Why do we recommend it?
Obkio is recommended for its intuitive UI and efficient network performance monitoring capabilities. It excels in identifying and pinpointing network issues, particularly for VoIP, video, and other critical applications.
Who is it recommended for?
This software is best suited for larger networks and Managed Service Providers (MSPs) seeking a reliable tool for continuous monitoring and quick troubleshooting of network performance issues.
Pros:
- User-Friendly Interface: Features an aesthetically pleasing UI for easy administration.
- Alert Variety: Enables customization in how performance issues are communicated.
- Device Compatibility: Runs seamlessly across desktop and mobile platforms.
- Efficient Problem-Solving: Reduces time spent identifying network problems.
Cons:
- Target Audience: More suited for larger networks and Managed Service Providers.
Obkio is a software application designed for monitoring issues like VoIP, video, and any application download. Obkio alerts you as soon as a problem occurs and pinpoints the source of the issue.
3. Auvik
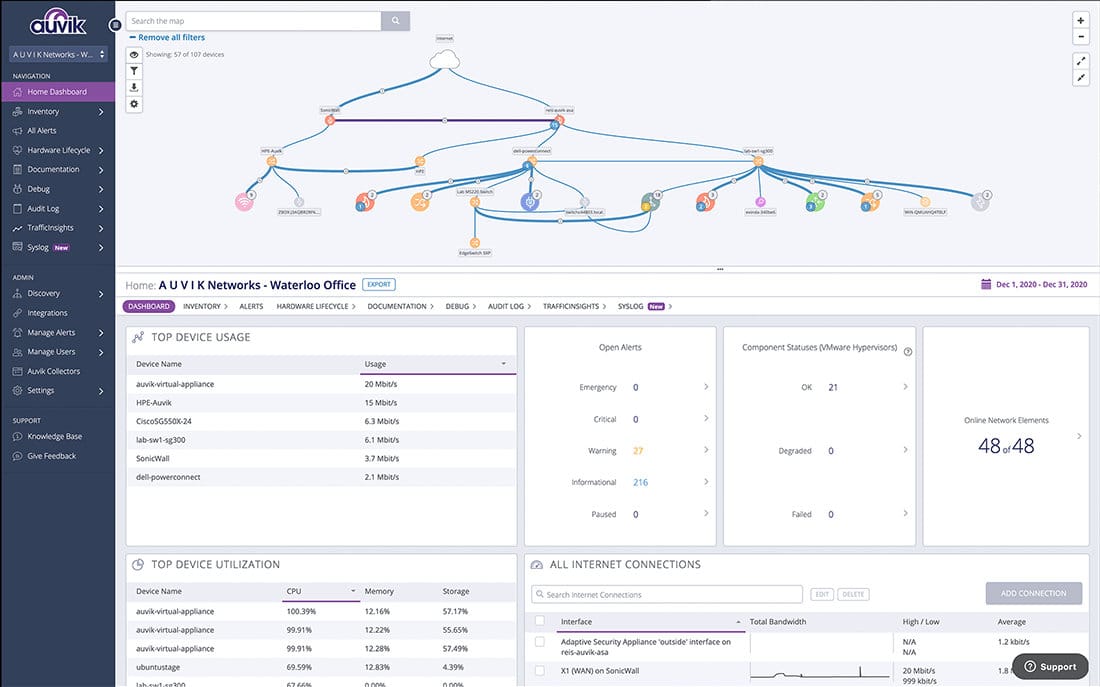
Auvik is a cloud-based platform for a network management solution and provides all the issue-related details across all the sites through a single dashboard. In addition, this tool has capabilities to manage and monitor multi-vendor network gear.
Key Features:
- Cloud-Based Management: Single dashboard for comprehensive site-wide network insights.
- Multi-Vendor Monitoring: Supports a variety of network devices for efficient oversight.
- Automatic Discovery: Keeps device inventories up-to-date seamlessly.
- CPU Monitoring: Threshold alerts for proactive performance management.
- Traffic Analysis: Quick identification of network anomalies for swift resolution.
Why do we recommend it?
Auvik is highly recommended for its cloud-based approach to network management, providing an easy-to-navigate interface and effective multi-vendor network monitoring. Its autodiscovery feature ensures that device inventories are always current and accurate.
Auvik offers constant device status checks with the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). Any problems identified with network device components provoke notification in the Auvik dashboard, so network managers can head off performance problems. However, if the network runs in a sub-optimal manner, subscribers to the Performance edition can use flow protocols to track traffic behavior and identify overloaded devices.
Who is it recommended for?
Auvik is best suited for IT professionals and network managers who need a comprehensive, yet user-friendly tool for monitoring and managing network operations across multiple sites and vendors.
Pros:
- Intuitive Interface: Navigating through Auvik is straightforward, enhancing user experience.
- Autodiscovery Feature: Ensures an accurate reflection of network devices in real-time.
- Performance Alerts: Sets thresholds for CPU monitoring to preempt issues.
Cons:
- Support Limitations: The open-source variant falls short in support compared to paid versions.
- Complex Setup: Installation may present challenges due to its technical nature.
It has an automatic backup configuration facility and is also considered a traffic analysis tool that helps identify anomaly detection faster. The primary functions of Auvik include the discovery of distributed IT assets, insight into network configurations, and network data encryption with AES-256.
You can register for a 14-day free trial.
4. Ping
The ping troubleshoot tool verifies the reachability to the destination host at the remote end by using IP ICMP echo requests. Ping comprises two messages. One is data packet competent that receives and sends the notifications from the destination IP address. The second type is the RTT process time (RTT =Round trip type and measured in milliseconds).
Here is an example of RTT:
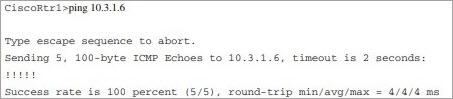
The above exclamation is an example that shows that ping is successful. If you get a notification saying that the destination is unreachable, it is an issue/error.
Key Features:
- Reachability Testing: Simple method to check host availability using ICMP echo requests.
- Lightweight Tool: Minimal system impact, ideal for quick diagnostics.
- Widely Accessible: Native integration with Windows environments.
- Well-Documented: Extensive resources available for troubleshooting guidance.
Why do we recommend it?
Ping is a fundamental tool for network troubleshooting, offering a simple and straightforward method to verify the reachability of a destination host. It's lightweight and widely documented, making it a reliable basic diagnostic tool.
Who is it recommended for?
Ping is ideal for users in any Windows environment who need a quick and easy way to check network connectivity and identify basic reachability issues.
Pros:
- Easy Diagnostics: Offers a straightforward approach to network troubleshooting.
- Minimal Resource Use: Incredibly lightweight, imposing no significant system burden.
- Universal Compatibility: Seamlessly operates within all Windows environments.
- Comprehensive Guides: Abundantly documented for user reference and learning.
Cons:
- Limited Scope: Not designed for continuous network monitoring.
- Visualization Absence: Lacks capabilities for data presentation and analysis.
5. Traceroute
The traceroute tool sends the ICMP echo requests to step by step in the IP address TTL (time to live) values. For example, suppose the starting value indicates the data packet it sends forward, and then each TTL value decreases by 1. The route rejects the data packet if the TTL value is zero.
Again, the source host sets the TTL value to 2 and, this way, the process will continue until the data packet reaches its destination and the destination host receives the ICMP echo reply message.
Key Features:
- Path Discovery: Maps the journey of data packets to the destination, revealing network paths.
- Built-In Utility: Directly accessible via the Windows command prompt for ease of use.
- Simple Operation: Utilizes a straightforward syntax for user convenience.
- Bottleneck Identification: Helps locate slowdowns in the network route.
Why do we recommend it?
Traceroute is recommended for its ability to map the path data packets take to reach their destination. This tool is invaluable for identifying where bottlenecks or failures occur in the network.
Who is it recommended for?
Traceroute is suitable for users who need to understand the gateways through which their network traffic passes, especially when diagnosing route-specific issues.
Pros:
- Integrated Access: Natively included in Windows, facilitating immediate use.
- Ease of Use: Features uncomplicated syntax for straightforward operation.
- Traffic Path Visualization: Shows the exact gateways traffic passes through.
- Bottleneck Spotting: Assists in identifying route-specific slowdowns effectively.
Cons:
- Reactive Monitoring: Not designed for preemptive network performance assessments.
- Limited Reporting: Offers basic output without extensive analysis options.
The main functions of the trace root include: each router will record every data packet, destination notifications, and calculate the latency.
6. Protocol Analyser
A protocol analyzer is an advanced tool used to identify network issues. This software intercepts and records the data packet flow between the source and destinations. For example, suppose your system is running slow; this tool helps us track the latency issues and other network diagnosing problems.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Traffic Analysis: Captures and analyzes data packet flow for detailed insights.
- Audit Capability: Suitable for both continuous monitoring and specific network audits.
- Network Overview: Offers a complete view of network activities for informed decision making.
Why do we recommend it?
A Protocol Analyzer is essential for in-depth network analysis, providing detailed insights into the data packet flow within the network. It's an advanced tool for diagnosing latency and other network issues.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is recommended for IT professionals with technical expertise who need to conduct comprehensive network audits or continuous monitoring for complex network environments.
Pros:
- In-Depth Traffic Inspection: Gathers detailed data across the network for thorough analysis.
- Flexible Monitoring: Adapts to continuous or targeted audit needs seamlessly.
- Holistic Network Perspective: Provides a broad overview of network behavior and performance.
Cons:
- Expertise Required: Demands a high level of technical knowledge for effective use.
- Data Volume: Handling and interpreting the extensive data captured can be challenging.
Final Thoughts
This post helps IT people, networking people, and NON-IT, common people. The Network problem is an everyday issue, and most of us have been experiencing issues such by trying all the strategies. This troubleshooting network connection problem is mainly designed for all readers struggling with the steps or configurations. In this post, we have explained the basic to advanced concepts like overview, what causes the networking connection issues, flow chart, techniques to solve them, and the popular tools used to resolve the networking issues. We hope this kind of post helps all the communities worldwide and tech experts.
Troubleshoot Network Connectivity FAQs
What are some common causes of network connectivity issues?
Common causes of network connectivity issues include misconfigured network settings, faulty hardware or cabling, software bugs or glitches, network congestion or bandwidth limitations, and security or access restrictions.
What are some steps to troubleshoot network connectivity issues?
Some steps to troubleshoot network connectivity issues include checking network cables and connections, verifying network settings, resetting network devices, checking for software updates or patches, testing network performance, and scanning for malware or viruses.
What tools can be used to troubleshoot network connectivity issues?
There are many tools that can be used to troubleshoot network connectivity issues, including ping and traceroute tools to test network connectivity, network sniffers to capture and analyze network traffic, and network monitoring tools to track network performance and identify issues.
What are some best practices for network connectivity troubleshooting?
Some best practices for network connectivity troubleshooting include starting with the basics (like checking cables and connections), working systematically to identify and isolate the issue, testing one thing at a time, documenting changes and results, and involving others (such as network administrators or support staff) as needed.




