Nagios is a fully comprehensive network and Infrastructure Monitoring suite that can help you to monitor everything on your network from server and workstation connectivity, to individual application and service monitoring on servers, in both Windows and Linux environments.
There are many features that Nagios has on board, and exploring every option and feature will take many articles to cover.
So for this run down, we will be looking at the basics of Nagios, and compare it to well the well-known monitoring application, Cacti. You can also compare Nagios vs Icinga in another of our blog posts.
Cacti began life as a graphical logging tool that was designed to monitor and collect data about network devices, and was built upon the foundations of RRDtool.
As the years passed, Cacti developed better features and a decent user interface, and it managed to remain as an open-source monitoring project that continues to actively develop new features to this day.
We will compare some of the features that these two different monitoring tools offer, and see which one you could use depending on your particular network monitoring requirements, and budget.
Nagios XI
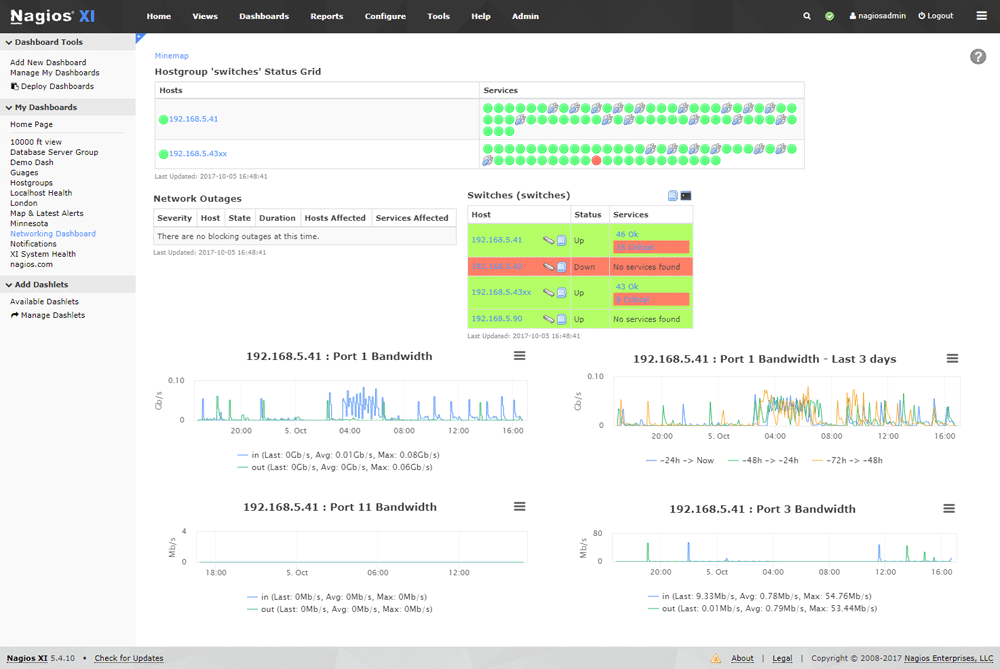
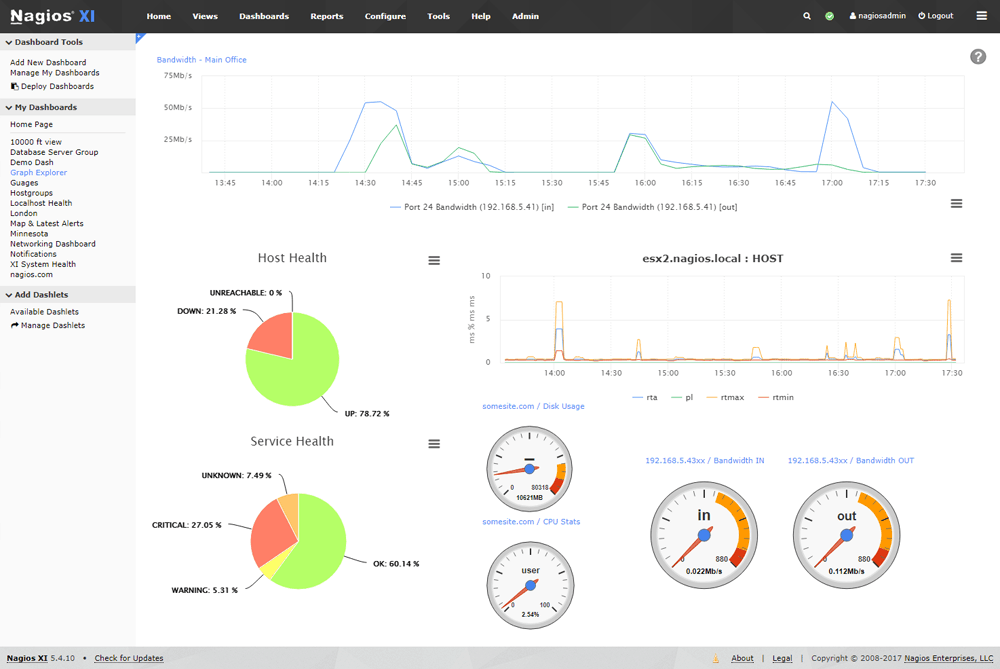
Nagios makes use of its powerful Nagios Core, which allows it to efficiently monitor systems and resources, even while scaling. It features a modern web interface that offers dashboards and high-level overviews of information such as hosts, services and network devices.
Key Features:
- Powerful Core Monitoring: Leverages the robust Nagios Core for efficient system and resource monitoring, ensuring scalability.
- Modern Web Interface: Features a contemporary web interface with dashboards for a comprehensive overview of hosts, services, and network devices.
- Advanced Visualization: Offers sophisticated graphing capabilities for real-time data analysis, ideal for management reporting.
- Capacity Planning Tools: Includes automated trending and capacity graphs for informed decision-making on upgrades and network expansion.
For those that work better with visualizations, there is an advanced graphing and meter section that lets you look at data in real time as a digital gauge, graphing, and as charts, especially useful for reporting to management.
Nagios offers unparalleled capacity planning via its automated and integrated trending and capacity graphs, which will give your decision makes all of the information that they need to make a well informed decision when planning upgrades throughout the organization and on your network.
Pros:
- Open-Source Flexibility: Provides transparency and customization potential through its open-source nature.
- Intuitive Dashboard: The interface is straightforward yet informative, facilitating easy navigation and data interpretation.
- Versatile Alerting: Supports a range of alerting options, including SMS and email, for flexible notification preferences.
- Developer-Friendly: Features a robust API backend, allowing for seamless integration with custom applications.
Cons:
- Support Limitations: The open-source version may lack the comprehensive support available with paid versions.
- Complex Setup: The installation process can be intricate, posing challenges for those without technical expertise.
While this all sounds quite complicated, it actually couldn’t be any easier to setup. Configuration wizards will semi autonomously work to get you up and running in next-to-no-time, and is all done with a few simple mouse clicks.
Infrastructure management is achieved easily, and features such as bulk host imports, auto discovery are all at your fingertips.
Nagios Additional Features
https://www.nagios.com/resources/nagios-core/
https://www.nagios.com/products/nagios-xi/#features
Cacti
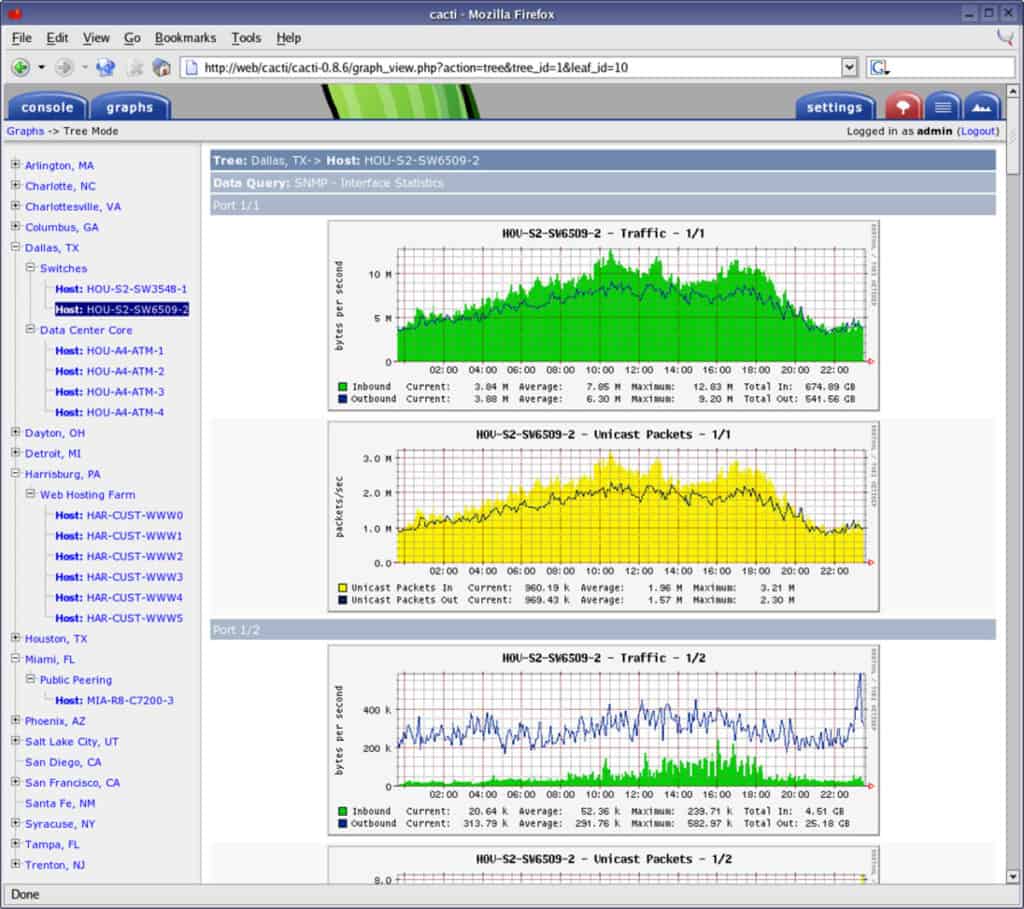
Cacti has a decidedly old school feel to it, and it is not surprising, seeing that it has been in development since around 2001!
But don’t let its simplicity fool you: it is still a rock solid monitoring platform that will quietly capture data on your network without any real intervention from a human operator.
Key Features:
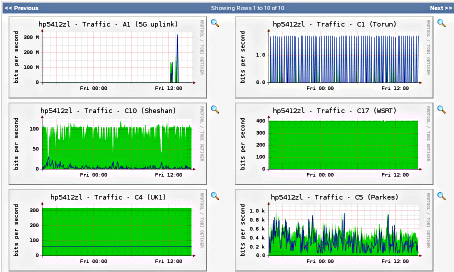
- Unlimited Graphing: Allows for the creation of endless graphs to monitor numerous network targets using internal data sources.
- Graph Sequencing: Enables custom monitoring zones with graph sequencing for tailored data visualization.
- Built-In SNMP Support: Utilizes various SNMP tools to efficiently gather information from network devices.
Cacti has many useful features, such as an unlimited graph creation tool, which means that you can monitor as many specific targets on the network as you like, by utilizing data sources and SDEFs from within the application itself.
Graph sequencing can also be accomplished through the application, allowing you to create a custom monitoring zone for easy viewing.
Cacti has built-in SNMP support, and it uses a combination of php-snmp, ucd-snmp and net-snmp to gather your network device information.
Pros:
- Customization Galore: Highly customizable, focusing on detailed data visualization to suit any monitoring need.
- Vibrant Community: Boasts a large, dedicated community offering extensive support and resources.
- User-Friendly Interface: Despite its complexity, offers a straightforward interface for easier navigation and use.
- Researcher-Friendly: Provides unmatched flexibility for data collection, making it ideal for research applications.
Cons:
- Learning Curve: Presents a more challenging learning curve compared to similar tools.
- Limited Support: Lacks the formal support options typically available with paid products, a common trait among open-source platforms.
Those with scripting knowledge can put their skills to work within Cacti, allowing them to grab even more SNMP data from the network.
For environments where security is important there is also a hierarchical user permission setup that limits access to lower level users, and opens up all functionality to admins and power users.
Cacti Additional Features
https://www.cacti.net/features.php
Nagios vs Cacti: What are the Main Differences in 2025?
|
Nagios |
Cacti |
|
| Network Scanning, Auto Discovery, Mapping & Visualization Maps |
✔ |
X |
| WMI, ICMP, SNMP |
✔ |
✔ |
| DB Functionality and Alerts |
✔ |
✔ |
| SLA Monitoring |
✔ |
X |
| Hardware Monitoring |
✔ |
✔ |
| Web Server Monitoring |
✔ |
✔ |
| Active Directory Alerts and Monitoring |
✔ |
X |
| Reports and Graphs of Historic Trends |
✔ |
✔ |
| Smart Device App: iOS, Android |
✔ |
X |
The uses for these two application are quite different, as Nagios is the more modern of them both, with more features and functionality to go around when compared to Cacti.
Cacti is a straight forward logging and graphing tool that would be used to good effect in an industrial or technical setting, where rudimentary data is required for reports, graphs and presentations.
The fact that it is open source also means that it can be used without costing the company where it is installed any money, which is a big bonus in these trying economical times.
The star of the show is Nagios, however, as its features, modern interface, and excellent plugin selection make it a more modern and much better choice for a modern enterprise that wishes to monitor their IT infrastructure on the network.
There is no limit to the amount of scaling that can be achieved on this platform, and the overall monitoring and alerting system is top notch as well.
Nagios is available from a 100 node monitoring system, all the way to an unlimited node installation.
These nodes are basically connectors to any device that has an IP address, which allows Nagios to scale up when monitoring IT infrastructure.
If your network needs constant monitoring then you will love the capabilities that Nagios has.
Nagios is not free, and must be paid for, but as an added bonus each license includes its own support contract that is valid for 12 months, which is great if you need any help along the way.
Nagios offers a standard edition as well as an enterprise edition, and each has its own positives and negatives, so you will need to choose what is right for your needs within your current setup.
Standard edition can be purchased through this link and Enterprise edition can be purchased through here.
Either of these applications could suite your particular needs better than the other, but it all depends on your intended uses for them, and what your budget is.
If you are hoping to monitor a few simple servers or applications and need to keep comprehensive logs, as well as char data for up-time reports and data analysis, then Cacti is definitely a good choice.
However, if you need a deeper level monitoring suite that can give you real time alerts and a library of specialized plugins for unique monitoring requirements, then Nagios might be the better choice for you.
Nagios vs Cacti FAQs
What is Nagios?
Nagios is an open-source monitoring system that provides real-time alerting, event handling, and reporting for network and server infrastructures.
What is Cacti?
Cacti is an open-source network graphing tool that provides real-time monitoring and graphing of network devices and applications.
What are the differences between Nagios and Cacti?
Nagios focuses on monitoring and alerting for infrastructure and applications, while Cacti focuses on graphing and trending of network and system performance data. Nagios is more customizable and flexible, but Cacti is easier to set up and use.
Which tool is better for monitoring and alerting?
Nagios is better suited for monitoring and alerting, as it provides more advanced alerting capabilities and can monitor a wider range of infrastructure and applications.
Which tool is better for graphing and trending?
Cacti is better suited for graphing and trending, as it provides a more user-friendly interface for visualizing network and system performance data.
Can Nagios and Cacti be used together?
Yes, Nagios and Cacti can be used together to provide a comprehensive monitoring and graphing solution. Nagios can be used for monitoring and alerting, while Cacti can be used for graphing and trending.
Is Nagios or Cacti easier to set up and use?
Cacti is generally considered easier to set up and use, as it provides a user-friendly web interface and requires less configuration.
Which tool is more customizable?
Nagios is more customizable, as it provides more advanced configuration options and can be extended with plugins and add-ons.
Which tool is more suitable for larger environments?
Nagios is more suitable for larger environments, as it can scale to monitor thousands of hosts and services, while Cacti is better suited for smaller environments.
Are Nagios and Cacti free?
Yes, Nagios and Cacti are both open-source and free to use. However, some plugins and add-ons may require a license or subscription.




