You may be wondering what the heck a ping sweep tool is at this moment, so let us explain. It is a tool that quickly and easily gives you live data relating to your IP address allocations on the network. It will give you feedback about the computers that are currently connected and transferring data on the network. It helps you to weed out DHCP addresses that are still allocated, but have become inactive.
We have gone ahead and compiled a list of what we think are the best ping sweepers available right now, and we hope that we can show off the pros and cons of each one, allowing you to make the best choice based on our deep dive into this information.
Here is our list of the best ping sweep tools:
- SolarWinds Switch Port Mapper – EDITOR'S CHOICE This tool is part of the Engineer’s Toolset, which is a package of more than 60 system management utilities. Use this tool to discover each switch and list the connected device for each port. Start a 14-day free trial.
- SolarWinds IP Address Manager- FREE TRIAL This is a component of the SolarWinds IP Address Manager Suite and is a very powerful tool. Download a 30-day free trial.
- Paessler PRTG – FREE TRIAL This is an application that sweeps for all active IPs on a set range. It is very useful for trying to find out more information about active IP addresses on the network. Download a 30-day free trial.
- ZenMap Has been around for quite a while, and it runs on multiple operating systems such as Linux and Windows.
- Fping – This is a command line tool for Linux that gives you great results without needing to write complicated scripts in the CLI.
- Network Pinger This is a great free tool that is simple yet powerful. If you need a simple IP sweeper then this app will get you over the finish line.
- Hping This is another free tool for pinging IPs on the network, with multiple Operating System compatibility.
- Angry IP Scanner This is another simple to use free tool for Windows, Mac and Linux. It gives you the option to specify IP ranges so that you can find the right addresses when you need them.
- Advanced IP Scanner This is one of the most popular free IP scanners, and its user base is pretty impressive. It offers a clean user interface that is simple and powerful.
- NetScan Tools Basic Edition If you don’t mind putting up with ads for a basic ping sweeper, then this is a viable option.
- Pinkie This is more of a network analysis application but it certainly offers ping sweep functionality
- Mitec Network Scanner This is part of a larger toolkit that provides users with many different tools, including a, you guessed it, ping sweeper.
Technical Breakdowns
We have dived into a lot of information in our product comparisons, so it seems fitting that we go into a little more detail about what each of the utilities and commands actually do in a little more detail.
Ping
PING is as part of the ICMP stack and is a connectivity function. It is present on most operating systems that incorporate TCP into their networking subsystems. Ping is therefore one of the very first commands that are used when connectivity troubleshooting starts. By using Ping you are able to establish whether or not the target device is online and responding.
Echo request. Echo response
Ping uses a special type of packet that has something called an echo request. Once the echo request has been received it sends and echo response to the sender computer. Ping operates off of an address. Without it, Ping cannot describe where the reply message needs to be sent. This address can be either an IP address or a hostname/computer name.
When you are troubleshooting network connectivity with Ping you are able to test things like DNS functionality. If a website is offline, you can try pinging its IP address instead. If you are able to get a response from the IP address, then you might have some kind of DNS error. This is because DNS takes hostname information and references requests back to IP addresses.
Many of the ping sweep features that we now rely on through GUI windows are repeatable on the command line, but in script form. This requires a fundamental understanding of how to write scripts and use functions and loops. GUIs are really easy to use, and they require no additional knowledge.
Ping is still an invaluable tool, even though it is very old.
Traceroute
Tracert is another tool that we use often to troubleshoot networks and test connectivity. Tracert uses UDP packets to test the connections and the intervals between hops. This is a different way of communicating than what Ping does, which uses ICMP.
TTL is the main measurement between hops, but it doesn’t have any measurements of time. Tracert shows you how many routers it passed through on its journey to the destination IP that you specified in the command. ICMP uses a similar messaging system to Traceroute when transmitting messages back to the operator. If a router drops a packet, then this is how it is communicated to you.
Tracert is also usable as a way to map a network with some scripting. Many, of the apps that we have looked at today will use both tracert and ping together. The functionality between these two tools can provide you with a detailed map of your environment regarding IT infrastructure and network devices.
Port Mappers
Port mapping is done by leveraging the UDP and TCP protocols together. These report back on ports that are active and open. An open port that is unattended is a security risk and it needs to be closed off. Using a port mapper will alert you to these instances so that you can resolve it. Some systems block the ping request, and using a port mapper can tell you if the IP address is up and running even though the Ping command might have failed, indicating a downed host.
The best Ping Sweep tools
Our methodology for selecting ping sweep tools and software
We reviewed various ping sweep tools and analyzed the options based on the following criteria:
- An autodiscovery system to log all network devices
- A network topology mapper
- The ability to collect live network devices statuses by using SNMP
- A facility to analyze network performance over time
- Graphical interpretation of data, such as charts and graphs
- A free trial period, a demo, or a money-back guarantee for no-risk assessment
- A good price that reflects value for money when compared to the functions offered
1. SolarWinds Switch Port Mapper – FREE TRIAL
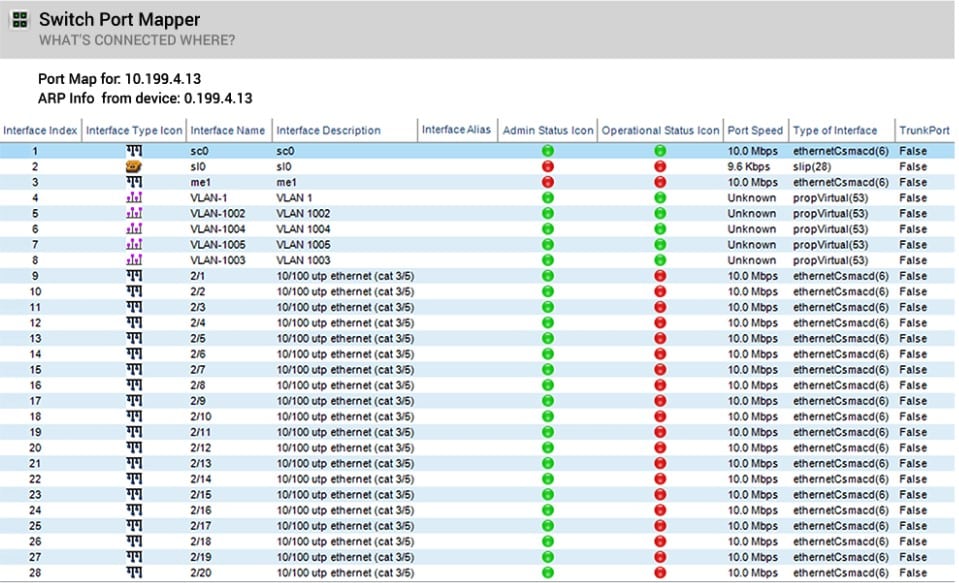
The SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset is a bundle of tools for system monitoring and management and it includes a Switch Port Mapper. This service adds an extra feature on top of device discovery because it scans each of the switches that it encounters and details the capacity and status of each port.
Unlike the other tools on this list, the Switch Port Mapper won’t identify all of the devices that you have connected to the network, so it won’t provide connectivity tests for computers, servers, firewalls, routers, or other network-connected devices.
Key Features:
- Detailed Port Capacity and Status
- Easy-to-Read Traffic Light System
- MAC and IP Address Visibility
- Packet Route Tracking
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Switch Port Mapper is an efficient tool for mapping and monitoring switch ports, aiding in device discovery, and troubleshooting port-related issues, especially helpful for network administrators and technicians.
The system will provide a map that shows how all the switches on your network link together. You will be able to see the MAC address and IP address of each of the devices connected to each port. An easy-to-read traffic light system shows a color-coded status symbol for each port.
The Switch Port Mapper provides troubleshooting tools so that you can work out what happened when communication on a port is showering as in error. The tool will also detail the time and date that the port stopped responding. You can use a packet route tracking tool to see how traffic crosses your network, passing through switches.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for network administrators who require detailed insights into the status and capacity of switch ports across their network, along with device connectivity and troubleshooting capabilities.
Pros:
- Easy to use, tools are self-explanatory and designed to get the job done quickly
- Includes a suite of other helpful tools, specifically designed for network administrators and on-site technicians
- Aids in device discovery and testing
- Can help verify DNS and DHCP functionality for different devices
- Can easily export or import results from previous scans
Cons:
- Would like to see a longer 30-day trial time
The Engineer’s Toolset is available for a 14-day free trial and that gives you free access to the Switch Port Mapper. You can also get an online quote.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
SolarWinds Engineer's Toolset is one of my favorite tools This is a really useful utility because it focuses on switches, which provide the glue to stick your network together. Focusing on switches helps me identify the really important hardware that keeps my network going.
Download: Get a 14-day FREE Trial
Official Site: https://www.solarwinds.com/engineers-toolset
OS: Windows
2. SolarWinds IP Address Manager – FREE TRIAL
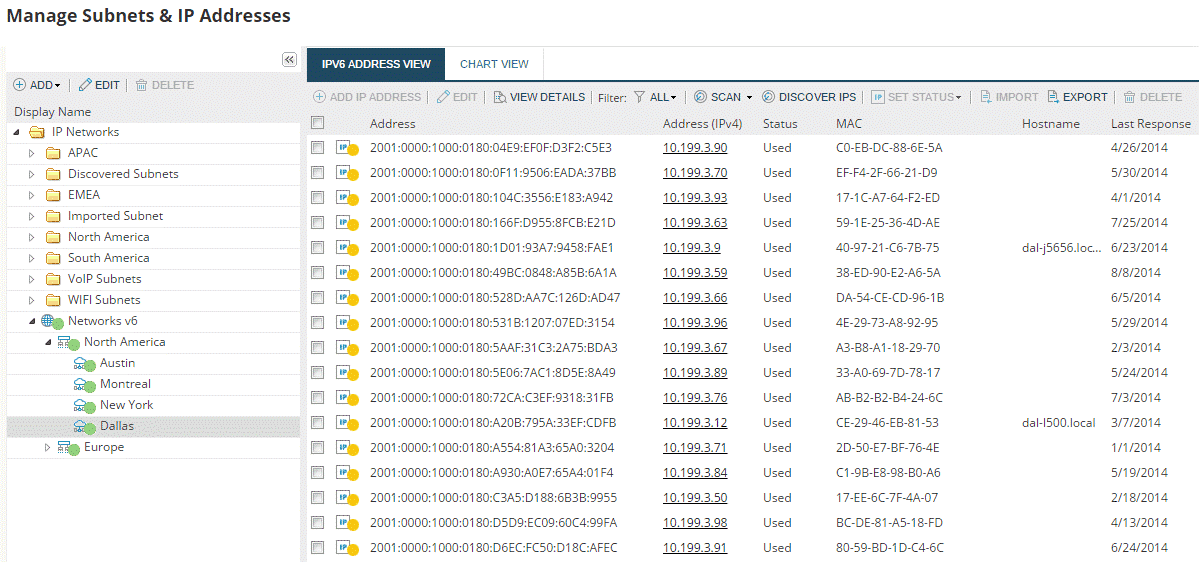
Any IP Address Manager worth its salt has Ping Sweeping capabilities, and this example is no different. Not only does it perform basic ping sweep functions, but also IP address management features too. This is especially useful if you have a large network where constantly running IP Sweeps from a single computer is not particularly effective.
Key Features:
- Ping Sweeping Capabilities
- Continuous IP Address Scanning
- DHCP Server Communication
- IPv4 and IPv6 Support
Why do we recommend it?
The SolarWinds IP Address Manager excels in IP address management and ping sweeping, making it highly effective for large networks that require continuous and automated IP address tracking and management.
This tool forms part of the IP Address Manager Suite. Much like PRTG, this tool uses a combination of ICMP and Ping to provide accurate and up-to-date information relating to your network and IP addresses. The scanning processes run in the background without any user intervention, which means it can run in perpetuity. Even better is that it updates you on the available IP addresses in your IP pool. It works with IPv4 and IPv6, so it is future-proof.
There is a dashboard with up-to-date stats about all of the network activity within your environment that changes whenever there is additional activity. It communicates with your DHCP server and updates DNS records so that any dead or expired IP addresses are recycled and allocated when they are needed. This leads to better performance and helps to clean up the network in general.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is particularly beneficial for sysadmins managing large networks, needing continuous monitoring of IP addresses, and automated management of DHCP and DNS records.
Pros:
- Simple interface that scales well even on larger networks
- Provides a continuous live look into your network – recording address status
- Can run automated tests to alert sysadmin when devices come back online
- Highlights issues such as rogue DHCP servers and IP conflicts
- Consolidates IP, DHCP, and DNS information into a single view to help shorten troubleshooting time
Cons:
- The tool is designed for sysadmin, home users will likely not use all tools and features
There is a free download link – it is active as a trial for 30 days, after which you have to purchase it.
3. Paessler PRTG – FREE TRIAL
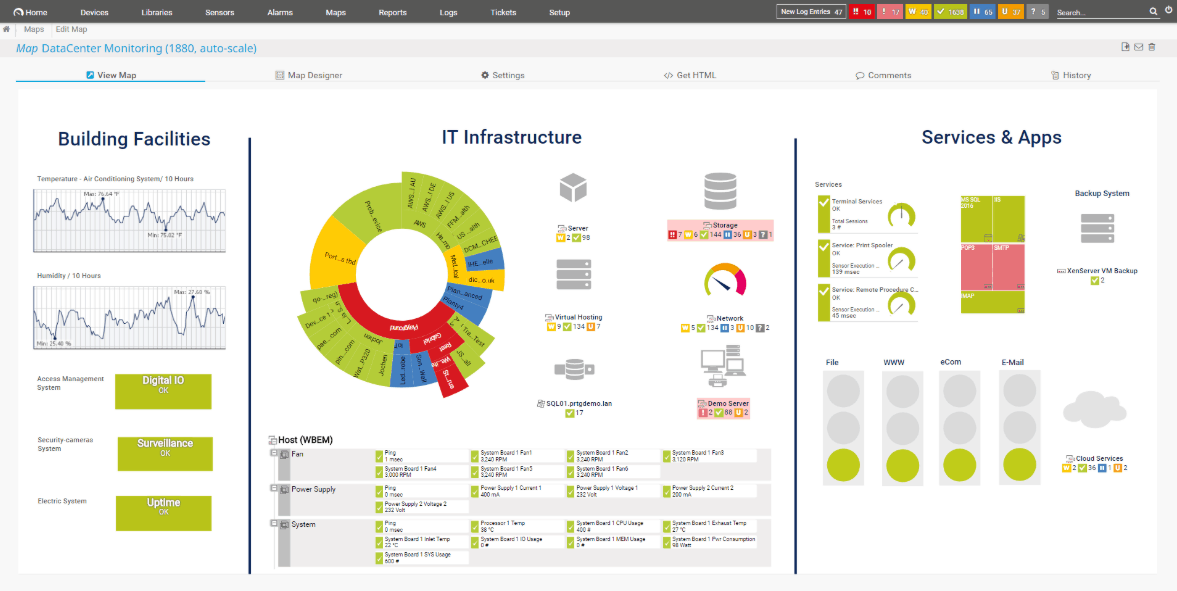
Paessler PRTG fully functional network scanning and monitoring suite. PRTG is capable of monitoring a wide range of items including computers, servers, web servers, applications. If you have cloud services that also need monitoring, then you can also use the Paessler PRTG configuration tool to set up monitoring for these services.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Network Monitoring
- Network-Map Generation
- Ping Sweep Integration
- SNMP Information Gathering
Why do we recommend it?
Paessler PRTG is a versatile network monitoring suite, offering extensive capabilities including ping sweeping, SNMP data collection, and dynamic network-map generation for real-time network visualization.
Most of the network diagnostics revolve around the ping utility, as these ICMP requests are the foundation of most network utilities. Right after installing the application, you will see that it begins scanning the network environment.
PRTG starts detecting and adding each device to your console, giving you a much-needed live view of the devices communicating on your network. Where PRTG is different from most of the applications in our list is that it can generate a network-map based on the IP ranges and latency of each host. This is a very useful way of mapping previously undocumented segments of your network. This scanning is all made possible thanks to a ping sweep.
Ping is a ubiquitous tool that is found in all systems that incorporate network functionality. This allows it to communicate across operating systems, vendors and manufacturers as it is a set standard.
Ping sweeping basically uses this technology and runs pings in a systematic and parallel way. Every response on the network generates an node on the monitoring console and will give you a target that you will be able to catalogue and label.
Ping sweep gets the ball rolling in the network discovery cycle. Once a ping response is received, the next step is for the SNMP routines to start probing compatible hardware and software for the appropriate tags. SNMP gleans a lot of specific information about each device, including serial numbers and manufacturer names. This cycle of detection runs constantly as long as the PRTG services are operating. This keeps all of the network information relating to your environment up to date.
PRTG is able to run as an on-site application on a physical or virtual machine, or online as a cloud service. Each computer or device that responds to a ping request is setup as a sensor in the application.
Who is it recommended for?
Recommended for IT professionals seeking a detailed and customizable network monitoring solution that offers a comprehensive view of their network's health and performance, across various devices and platforms.
Pros:
- Uses a combination of packet sniffing, WMI, and SNMP to scan IP addresses as well as measure device performance
- Fully customizable dashboard is great for both lone administrators as well as NOC teams
- Drag and drop editor makes it easy to build custom views and reports
- Supports a wide range of alert integrations such as SMS, email, and integrations into platforms like Slack
- Supports a freeware version
Cons:
- Is a very detailed platform with many features that require time to learn
The free version of this software comes with 100 sensors. There are different pricing structures for each segment of sensors that you need. If you’d like to try it out for yourself by downloading a 30-day free trial.
4. Zenmap
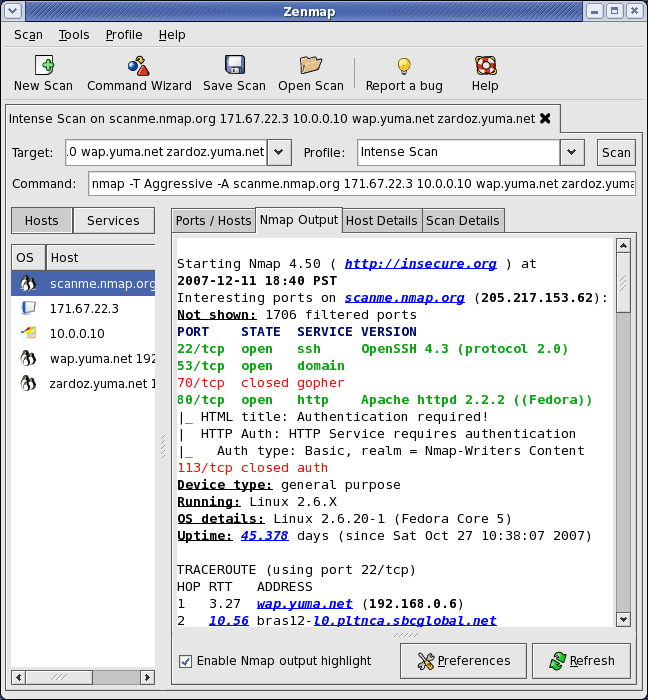
Most people have heard of Nmap, the multi-platform tool that runs on Linux, Windows and Mac OS. Zenmap is the extension of Nmap but with a graphical user interface that makes it easier to use for the average person. This makes it especially useful in environments where there is more than just one specific operating system as it can communicate across this barrier thanks to the ping sweep technology that is inherent in this style of application.
Key Features:
- Graphical User Interface for Nmap
- TCP and Ping Scanning
- Multiple Profile Support
- IP Address and Hostname Information
Why do we recommend it?
Zenmap simplifies network scanning and security analysis, combining the powerful functionality of Nmap with a user-friendly interface, making it accessible for both technical and non-technical users.
Zenmap uses TCP and ping together to allow for accurate mapping of your network. There is support for multiple profiles in Zenmap, so you can customize each of these views to suite the operation that you are carrying out. This means that the output of each scan will depend on the profile that you selected. The capabilities of this application allow you to pull both IP address and hostname information. When the scan is operating in TCP mode then you will be able to gather information about which ports are open on a target system. This is essential if you are trying to safeguard your network against unauthorized access.
You can decide on what kind of format you would like to look at in Zenmap, which means that technical users can dive in to the deep end of the data nd pull out all the details that are needed to make a case for a technical investigation.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for network administrators and security professionals in multi-platform environments who need a versatile, easy-to-use tool for network mapping, security auditing, and troubleshooting.
Pros:
- Doubles as a security tool, allowing administrators to discover open ports, and applications communicating over ports that are suspicious
- Massive open-source community, is one of the most popular free security tools available
- Offers a lighter CLI version called Nmap
- Doubles as a security tool
Cons:
- Nmap can have a steep learning curve for new users
Zenmap files can be stored and exported for further investigation and analysis. This application is free to use.
5. Fping
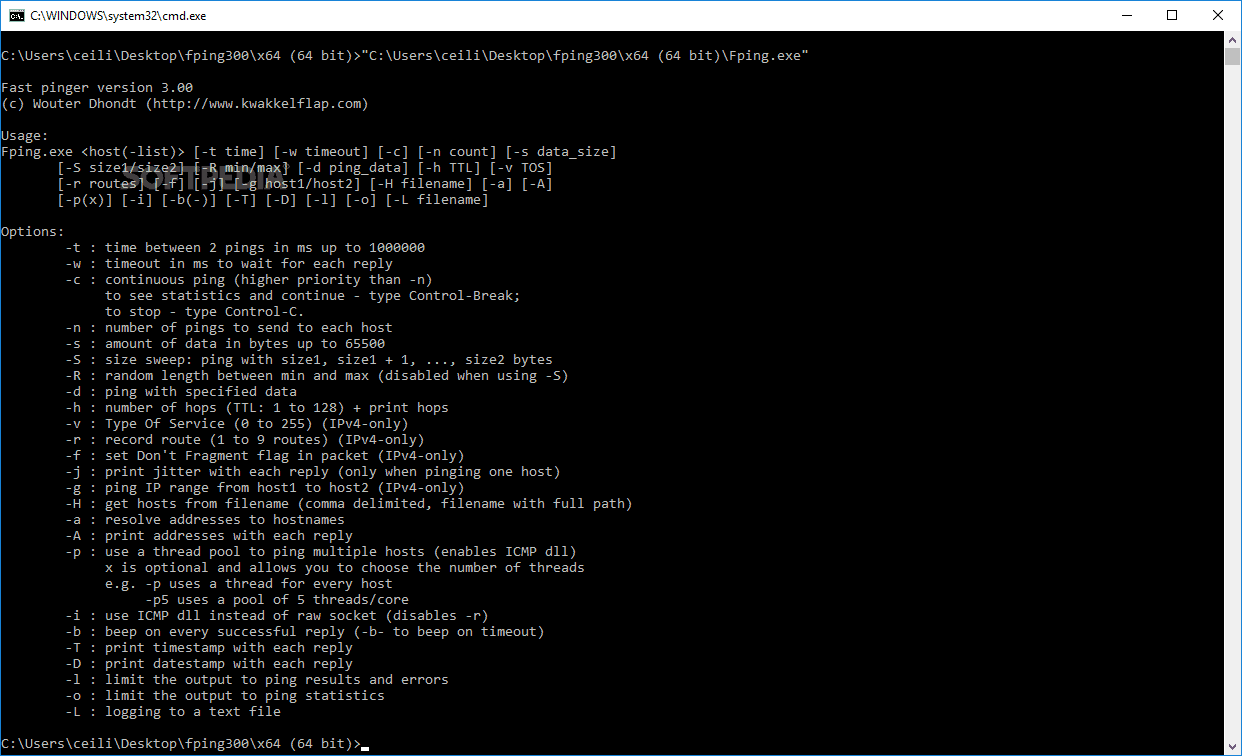
FPing is a non-graphical tool that runs in Linux directly from the command line. There is no graphical window so that means that you have to type everything manually. This is free to use and requires little bit of typing. You need to provide both the individual IP addresses that you wish to ping, as well as the ranges that you wish to sweep.
The easiest way to do this is to store the IP addresses that you wish to query in a text file. This can then output this file into fping so that it can start querying all the IPs on the network. Because this is based on a Linux tool you can pretty much pipe and grep commands so that you can find information out about your current IP setup.
Key Features:
- Command-Line Interface
- Supports IPv4 and IPv6
- Offline and Online IP Address Detection
- Direct DNS Records Communication
Why do we recommend it?
Fping is a flexible and efficient command-line tool, perfect for Linux users who prefer a text-based interface for conducting detailed and targeted ping sweeps across their network.
You can use switches with Fping so that you can either limit the range of IP addresses that you wish to, or change between IPv4 and IPv6 .The great thing about Fping is that it doesn’t limit itself to online IP addresses. Your queries will pull data back from multiple sources and shows you which IP addresses are offline or online. When issues are found, Fping ac communicate directly with the DNS records of your system. This way of doing things helps you to see issues with dead connections so that you can reclaim them back into the IP Pool.
FPing doesn’t run in the background, but instead relies on your cron task scheduler.
Who is it recommended for?
Best suited for Linux administrators and users comfortable with command-line operations, needing a tool for quick and extensive network analysis.
Pros:
- Easy to learn syntax, especially for heavy Linux users
- Reports are available in simple text format
- Can filter based on subnet or IPsec version
Cons:
- Only available for Linux
- No metric visualization, text only CLI tool
Get started with the free download.
6. Network Pinger
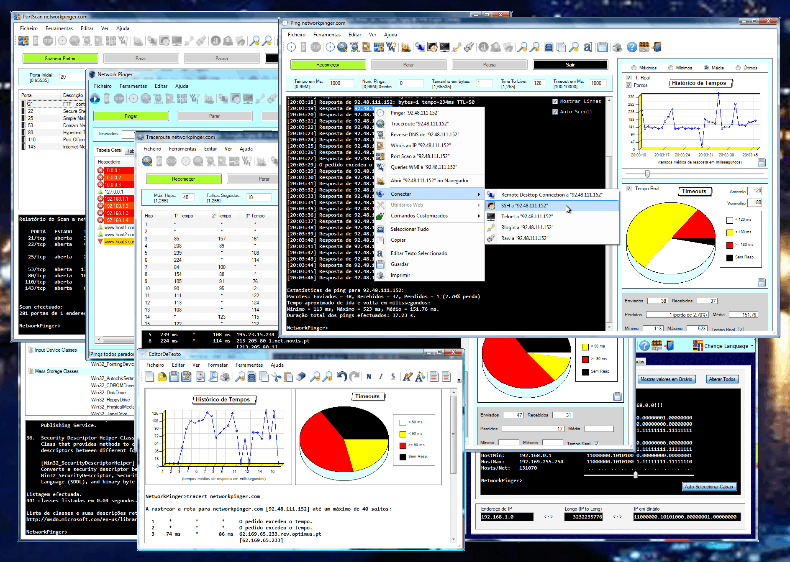
Network Pinger is another free tool, but this time one that runs on Microsoft Windows. All you need to do is input a range of IP addresses that you wish to ping and then wait for each response to come back.
There is a decent interface that shows the progress of each ping while giving its response for each target. Each response will give you an indication of the overall performance of the tests. The charts and graphics are a good way to visualize how many hosts are up or down, which is a lot more intuitive than trying to manually count from a list.
Key Features:
- Visual and CLI Ping Tracking
- IP Calculator and Switch Port Mapper
- Subnet Filtering
- Traceroute Functionality
Why do we recommend it?
Network Pinger offers a comprehensive set of features including visual ping tracking, subnet filtering, and additional network tools, making it a versatile option for network scanning and analysis.
A feature that you don’t see too much of with the other products is the ability to ping single IP addresses. Interestingly there is also a tracert and switch port mapper that come with this application, making it very useful. Additionally, there is also an IP calculator if you are wanting to do any subnet calculations and planning then you can take a look at this too. There are also some useful troubleshooting tools available to assist with anyone wanting to fix issues on a production network.
Who is it recommended for?
Recommended for network administrators and technicians using Windows environments who need a multifunctional tool for network scanning, troubleshooting, and planning.
Pros:
- Can track the pings visually as well as through CLI
- Includes an IP calculator and switch port mapper, a nice set of features not found in most other ping sweep tools
- Can scan larger networks and filter by subnet
Cons:
- The interface can get cluttered quickly
- Not the best tool for long-term monitoring
Access the download.
7. Hping
Hping is exclusively a command line utility, which means there is no GUI. This is not a problem for most experienced network administrators, but some people might find the lack of selectable graphics options to be a disappointment. Having this tool available on a system without xserver or another graphical renderer is probably where most people will find the most usefulness from it. It is a multi-platform application that works on Windows, Linux, Unix and Mac OS.
Key Features:
- Command-Line Network Tool
- TCP/IP Protocol Layer Functionality
- Traceroute Implementation
- Cross-Platform Compatibility
Why do we recommend it?
Hping is a lightweight, yet powerful network analysis tool, functioning primarily through the command line, ideal for detailed network scanning and troubleshooting.
Ping is just one part of many moving cogs in the ICMP stack. It functions within the Internet Layer around the TCP/IP protocol. What this means is that it lack sport visibility, which would allow for greater traffic analysis for target systems. Hping uses a series of serial ping requests to every IP address within a set of Ip addresses. If you are troubleshooting connectivity issues, then there is even a tracert implementation to test the path to your target device. You can identify where the issue is and take action from there, which is great.
As is the case with some command line style applications, you can send data output directly to other applications. For example, you can send data directly to grep and the query with a string of text to identify a name or target in the results.
Who is it recommended for?
Suitable for experienced network professionals and system administrators across multiple platforms who require a resource-efficient tool for in-depth network analysis and security testing.
Pros:
- Completely free tool
- Supports Linux, Mac, Unix, and Windows
- Lightweight, uses very little system resources
Cons:
- No visualization options
- Not many more features than using a Windows cmd prompt
Visit their download page.
7. Angry IP Scanner
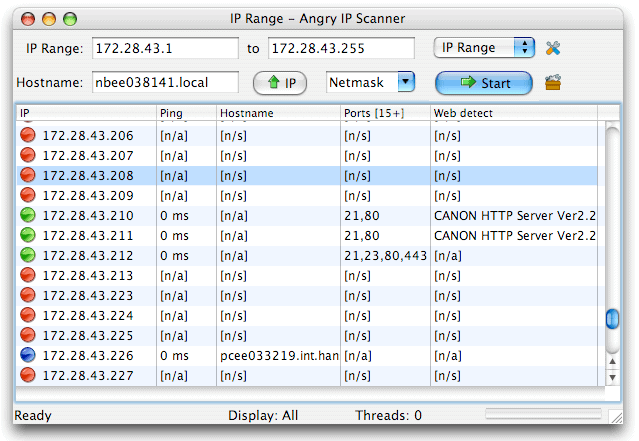
Angry IP Scanner is one of the easiest IP Scanners that you are likely to come across. It features an easy to read and use interface. What makes this application so popular is not just the ease of use. It is easy to use and is also free. It runs on Windows, Linux and Mac OS. The results are very easy to interpret and can be sorted by various headers in the table of results.
Key Features:
- Easy-to-Use Interface
- Supports Multiple File Formats
- DNS and Hostname Metrics
- Displays MAC Addresses
Why do we recommend it?
Angry IP Scanner is a user-friendly, fast, and efficient scanning tool, perfect for quickly identifying active and inactive IPs and gathering essential network information.
This is a great tool for finding unexpected IP addresses on your network. Once you have decided on which range you wish to scan, simply hit the start button and then wait for the results to come in. The output from this scan can be outputted straight to popular file formats such as CSV, TXT, XML or even IP-Port.
The app itself uses the DNS resolution status from your system which lets you know if a computer is online or offline. When you come across hostnames that are missing then you need to start investigating. The great thing about this scanning tool is the fact that you can also see the MAC address of each device. This is especially useful because some environments let you lock down access according to that physical address.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for users in small to medium-sized networks, including home users and small businesses, who need a simple yet effective tool for network scanning and analysis.
Pros:
- One of the easiest tools to use on the market
- Great for small networks and home use
- Can output in multiple formats, giving more flexibility than CLI tools
- Offers DNS and hostname metrics
Cons:
- The interface doesn’t scale well on enterprise-size networks
- Lacks graphing capabilities
This tool uses more than just simple ICMP technologies. It is able to display port and MAC address information as well, which is beneficial when you are trying to lock down the environment and close open ports that do not need to be open. Try it out for yourself and download it from here.
8. Advanced IP Scanner
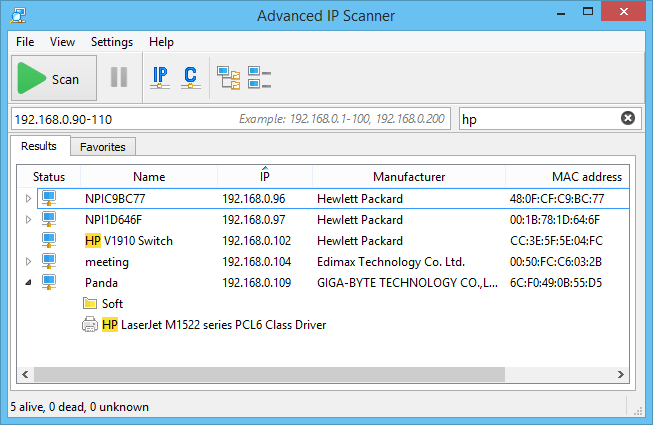
Advanced IP Scanner is available on Windows 10 and is free to use. It has very similar visual characteristics when comparing it to applications such as Angry IP Scanner, so it is easy to use. This is just like many of the other IP scanners on our list because all you need to do is enter the IP range that you wish to interrogate. If you feel like saving the scan data to your system, then you will find XML data generated for each scan. The results list also displays multiple other records to network shares that are accessible on every host that appears on the list. You can even see who the manufacturer is of each of the network cards.
Key Features:
- Easy-to-Use Interface
- XML Data Generation for Scans
- Network Shares Accessibility
- Hostname, MAC Address, and Manufacturer Information
Why do we recommend it?
Advanced IP Scanner is a user-friendly and efficient tool for scanning and managing IP addresses, providing essential network information and accessibility to network shares, making it suitable for smaller network environments.
If you are able to connect to the computer then you can browse the network shares and send other command to them as well. Additional exporting features will let you generate CSV files so that you can compare the data against your DNS records. Very useful features indeed.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for network administrators and technicians in smaller networks or home environments who need a straightforward, feature-rich tool for IP scanning and network management.
Pros:
- Free to use
- Very easy to use, great for smaller networks
- Provides hostnames, MAC address, and manufacturer statistics
- Simple interface, feels intuitive
Cons:
- Lacks multiple export formats
- Does not support graphing to visualize traffic or devices
- Not the best option for enterprise networks
The reason for this application’s success if the fact that it is easy to use, it looks good, and it is jam packed with features that make life that much easier for anyone trying to take control of their respective networks. Visit their download page.
9. NetScan Tools Basic Edition

This application comes in two different flavors: the commercial version and the free version. The free version has the ping sweeper functionality enabled, although this version has ads. This is done so that the ad revenue supports the development of the free version. If this is not a deal breaker for you then this application is quite useful.
Key Features:
- Ping Sweeping Functionality
- DNS Queries for Name Resolution
- CSV File Export for Results
- Latency and Hostname Information in Results
Why do we recommend it?
NetScan Tools Basic Edition offers essential ping sweeping and DNS query functions, with the ability to save and analyze results, making it a practical tool for basic network scanning and troubleshooting.
Ping scan requires that you enter is a range of IP addresses so that the scan can begin. Each of the hosts mentioned in your IP list will be contacted one by one, then the result will be returned back to the application. There is useful information in the results, such as latency and hostname information.
Much like all the other IP Sweep applications that we have looked at today there are a few standard features that we can expect from a decent example. You can save and store your results as a CSV file. If you analyze your data and notice that there are missing hostnames in your results then it could be pointing at a DNS issue. Be sure to check out your current address pools and make sure that expired hosts are actually offline. If not, then you could have a security breach.
Who is it recommended for?
Best suited for users on Windows 7, 8, and 10 who need a lightweight, no-frills tool for network scanning, especially useful in small to medium-sized network environments.
Pros:
- Offers a paid and free version, making it accessible for any budget
- Lightweight, the tool can be run on practically any endpoint
- Uses DNS queries to test name resolution and address scanning
Cons:
- The interface can feel outdated and a bit cluttered when scanning larger networks
- Only available for Windows operating systems
This is a decent application, but it is important to note that the free version is lacking some features when compared to the full version. The application only runs on Windows 7,8 and 10. Access it on their site.
10. Pinkie
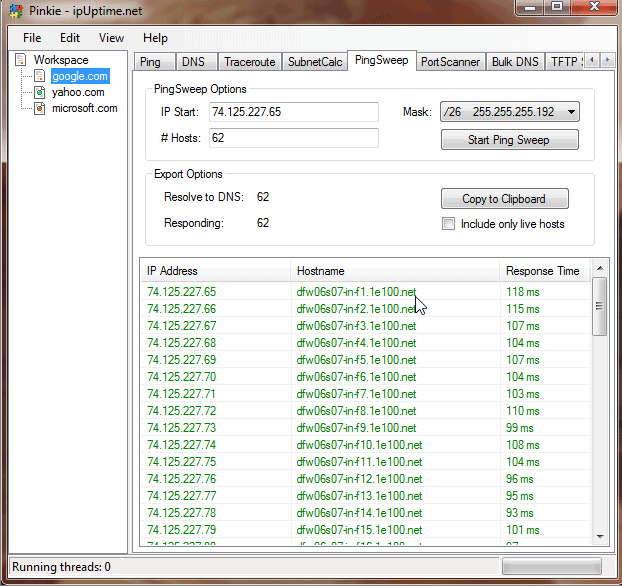
Pinkie is much more than just a Ping Sweeping utility. It offers Ping, DNS, Traceroute, Port Scanning, Bulk DNS and TFTP functionality all rolled into a single, simple application.
This application operates in a slightly different way to the others that we have looked at so far. There is an option to search for offline hosts as well as online ones. That means that the scan can continue searching and returning results even if the records that it is detecting are offline.
Key Features:
- Ping, DNS, Traceroute, and Port Scanning
- Search for Offline and Online Hosts
- Fast Scanning and Results Reporting
- Bulk DNS and TFTP Functionality
Why do we recommend it?
Pinkie is a comprehensive tool that combines multiple functionalities, including ping, DNS, and port scanning, into a single application, offering fast and accurate network scanning capabilities.
Pinkie works very fast, making short work of the scanning tasks that you set before it. Again, each result contains latency information, hostname data and return trip speeds. All of this information gives you an idea of what is actually happening on your network.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for home users or small network administrators who require a simple, all-in-one tool for network scanning, troubleshooting, and reporting.
Pros:
- Completely free tool
- Simple to use, good option for home users
- Can find addresses as well as report on external domains and servers
Cons:
- The interface is clunky, using arrows to show tabs that get hidden on the toolbar
- Lacks graphical tracking
- Limited reporting options
Overall, this is a very good tool that is fast to load and run and offers some additional features. Visit their download page.
11. Mitec Network Scanner
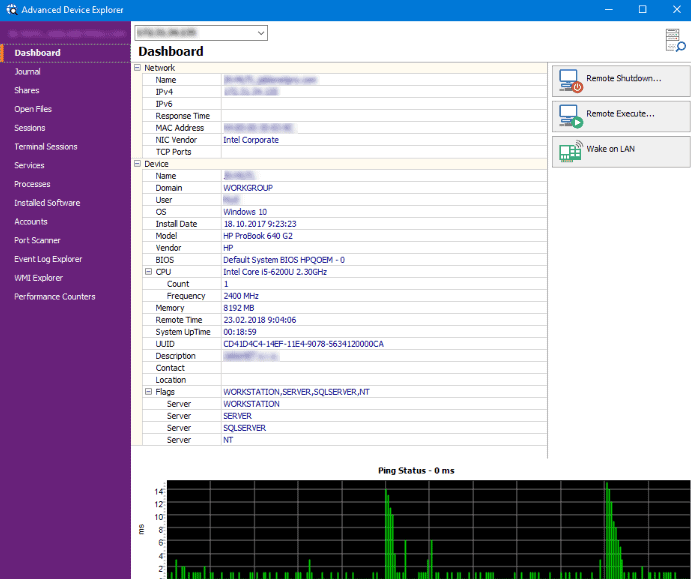
Mitec Network Scanner packs a lot of features under the hood. It gives you a ping sweeper that will identify the IPs that are active and inactive on the network. It offers port scanning, NetBIOS functionality, SNMP scanners, and much more.
Other features that are included in this application are: Active Directory, Network Neighborhood, Ping, IP Address, MAC Address, MAC Vendor, Device Name, Domain and Workgroup information, Logged in users, Operating System data, BIOS, Model and CPUs, System time and Uptime, device descriptions, type flags, TCP and UDP port scanning, and more.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Ping Sweeping
- Port Scanning and NetBIOS Functionality
- Detailed Network Information (Active Directory, Network Neighborhood, etc.)
- SNMP Scanners Integration
Why do we recommend it?
Mitec Network Scanner is a versatile and feature-rich tool, offering extensive network scanning capabilities along with detailed information about network devices, making it an excellent choice for in-depth network analysis.
You can export your ping sweep results for further analysis, and again, you can compare this information to your DHCP and DNS records to find any anomalies and strange behavior on your network regarding issued IP addresses and registrations.
Who is it recommended for?
Recommended for network professionals in Windows environments who require a multifaceted tool that provides detailed insights into the network infrastructure, including device information, port status, and more.
Pros:
- Does a great job at displaying ping metrics graphically and through verbose text
- Completely free tool
- Can run Whois lookups as well as DNS resolution on hostnames
- Great looking interface, easy to navigate even on larger networks
Cons:
- Limited to Windows operating system
- Would like to see more reporting options
- Is not open-source
Visit their download page.
Conclusion
We have gone through a lot of data in this article. There is a lot to learn about troubleshooting networks and scanning for IP addresses. Each of the products that we have looked at will provide you with different levels of usefulness, so your favorite might be very specific to your environmental requirements. There are some people that need lots of different free tools, while others only want a ping sweeper.
We hope that this information has been useful!
Related Post: Best Ping Monitoring Tools
Ping Sweep Tools FAQs
How does Ping Sweep work?
Ping Sweep works by sending ICMP Echo Request packets to a range of IP addresses and listening for ICMP Echo Reply packets. If a host responds to the ping, it is considered to be active and its IP address is added to a list of active hosts.
Can Ping Sweep be used for both IPv4 and IPv6 networks?
Yes, Ping Sweep can be used for both IPv4 and IPv6 networks by specifying the appropriate IP address range.
Is Ping Sweep a passive or active scanning technique?
Ping Sweep is an active scanning technique, as it sends ICMP Echo Request packets to the network and waits for responses.
What are some popular Ping Sweep tools?
Some popular Ping Sweep tools include Fping, Angry IP Scanner, Nmap, and SolarWinds Ping Sweep.