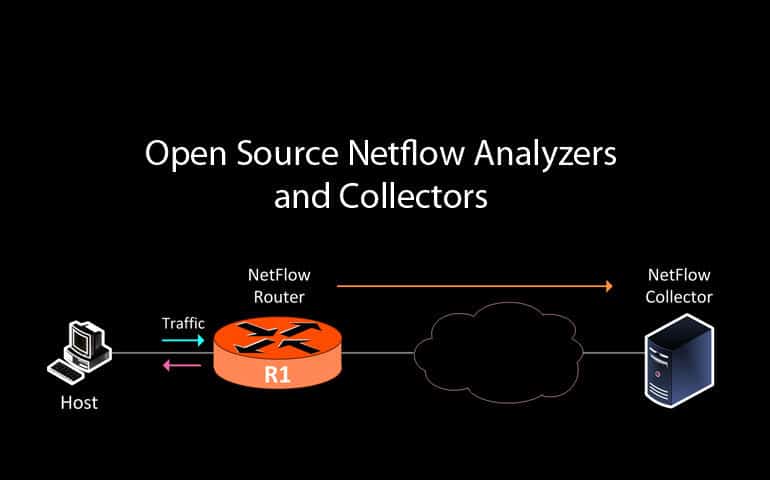
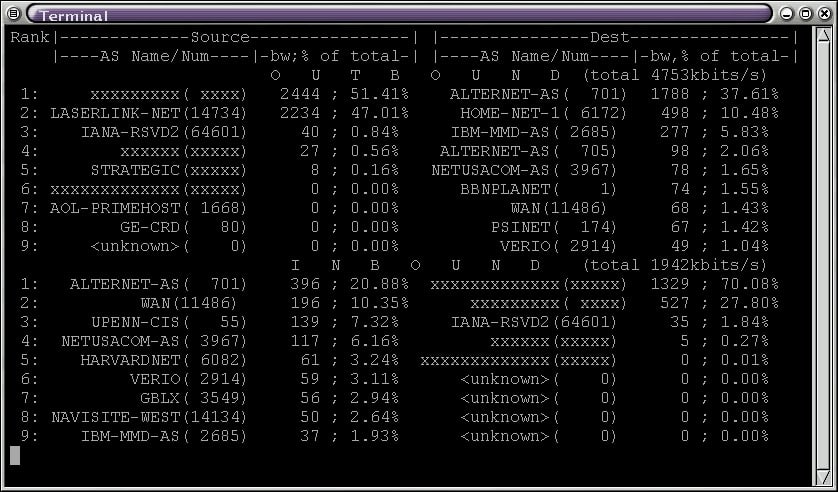
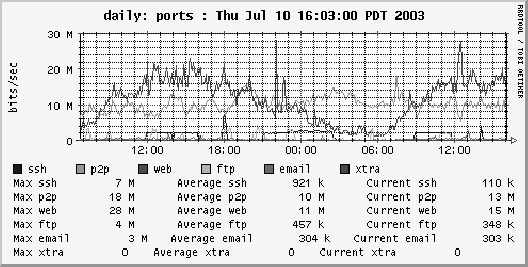
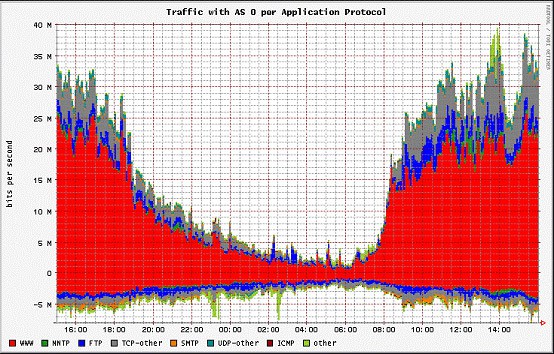
NetFlow analysis is undeniably powerful when it comes to assessing and analyzing your network, network traffic and bandwidth, devices, or just about anything to do with the data being transmitted over your network. There are a variety of tools which can assess traffic on a basic level in terms of round time and packet loss, but NetFlow allows you to discern so much more about each individual packet. What's more, levy that knowledge by means of analytic software and data aggregation via charts and graphs to dramatically ease your task at hand.
Here is our list of the best free open source NetFlow analyzers & collectors:
- Flowscan – Network traffic flow visualization and reporting tool that combines a flow collection engine, a high-performance round-robin database, and a visualization tool (RRDtool) to provide network border traffic views.
- Cflowd – Flexible tool that can sample IPv4, IPv6, MPLS, and ethernet traffic flows to provide insights into network trends and workloads in the environment of a network service provider.
- NTop – Comprehensive tool for capturing packets, recording traffic, analyzing traffic, and probing network packets for Windows and UNIX devices.
- EHNT – NetFlow collector and analyzer that works on version 5 only. It is well-suited for Linux and BSD devices.
- Flow-tools – Collection of programs used for collecting, sending, and processing NetFlow data. It can also be used for generating reports.
- BPFT – Traffic accounting daemon and data management tool that captures IP traffic.
- Panoptis – Handy tool that collects and analyzes NetFlow data to detect ad block DoS and DDoS attacks.
When it comes to almost any software need these days, there tends to be a wide range of options, both paid and free, and the open-source movement remains quite active.
Open-source software tends to have remarkable flexibility, either via child builds and projects that spawned off the shortcomings of their forefathers, or by means of exceptional modularity and transparency. That would be simply unheard of with any kind of paid, enterprise-level solution.
With that said, however, an open-source project is only as powerful and prodigious as its proponents.
Projects that go untouched or end up more or ‘less finished' tend to taper off as far as forward-thinking support and features, and can often fall behind the curve of usefulness if they become too deprecated, often in favor for different open-source options that are newer or built on a more current framework.
Open-source software in the NetFlow realm can be powerful indeed, but you have to be sure the solution you're looking at fits your networks needs and won't leave you wanting. If none of the solutions from below work, consider a commercially available Netflow Collector/Analyzer, some of which are free to use or have extensive trials.
The Best Free Open Source NetFlow Analyzers & Collectors
Our methodology for selecting open-source Netflow analyzers
We reviewed various NetFlow analyzers and analyzed the options based on the following criteria:
- Data integrations into other platforms
- Ease of use
- Support for various version of NetFlow
- Analyze network performance over time
- Graphical interpretation of data, such as charts and graphs
- Free trial period, a demo, or a money-back guarantee for no-risk assessment
- Good price that reflects value for money when compared to the functions offered
1. FlowScan
FlowScan is somewhat interesting in that it acts more as a generalized tool for visualizing NetFlow data rather than collecting and aggregating it for later analysis. By its very nature there's a slight delay, but it does an excellent job gathering up and displaying the NetFlow statistics for you to admire visually almost on the fly!
Key Features:
- Identifies the Nature of Network Traffic Provides a near real-time view of network traffic to help understand the nature of your internet traffic, allowing you to identify the source of thetraffic and keep the necessary checks in place to stop malicious content from entering your network.
- Examines Data Also maintains counters of metrics, and stores them in the RRDtool, a database system for time-series data.
- Generates Reports Analyzes the network data and generates reports according to Cisco’s NetFlow format. This data can be used for further processing as needed.
Why do we recommend it?
FlowScan examines Netflow data and maintains counters to make sense of the collected information. Also, it generates meaningful reports that provide precise information about your traffic.
The tool is most native to the GNU/Linux environment and requires a combination of collector and Perl script for the visual aspects, as well as a database component.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for GNU and Linux environments, and works well for network administrators who want reports on the processed flow data.
Pros:
- Provides detailed visualization options for Netflow data
- Users can build reports from collected data
- Supports live monitoring
Cons:
- Outdated when compared to similar tools available
- Not as easy to use as competing tools
- Live monitoring is delayed
Download link: https://www.caida.org/tools/utilities/flowscan/pub/
EDITOR'S CHOICE
FlowScan is our pick for an open-source Netflow analyzer because it is comprehensive and offers a graphical representation of the data. As a result, it’s easy to identify network traffic patterns and make informed decisions.
Download: Download FlowScan
Official Site: https://www.caida.org/catalog/software/flowscan/
OS: Windows, Linux
2. Cflowd
While Cflowd is no longer under active support and updates, it's still a pretty reliable offering that does all the basic collection, storage, and analysis of NetFlow data. It's a fairly barebones piece of software, but it does precisely what it needs to do.
Key Features:
- Highly Versatile Helpful for network engineers to plan their future capacity and understand network traffic trends for informed decision-making, can also help ISPs map their workflow characterization in their environment for better implementation and segmentation.
- Multiple Export Formats Exports data in many formats to suit different applications, as version 5 generates a fixed export record for every individual flow while version 10 creates a variable export record based on user configuration and sampled traffic type.
- Advanced Filters Check each packet against a specific set of filters, allowing you to forward the packets to the appropriate route.
Why do we recommend it?
Cflowd is a versatile tool for tracking the usage of web hosting, accounting, billing, network planning, data warehousing, and more. It analyses Netflow data across all these operations to provide in-depth insights.
It also has some modularity with a variety of other packages that can be used to modify what it can do and how to display data.
Who is it recommended for?
A good choice for ISPs and network engineers who are into capacity planning, trend analysis, and characterization of workloads.
Pros:
- Features tools to aid in capacity planning and trend analysis
- Simple install requirements
- Leverages flow dump for faster data filtering
Cons:
- Considered abandonware – no longer supported as of 2004
Download link: https://www.caida.org/tools/measurement/cflowd/download/
3. ntop
ntop is a solid choice that works well in both UNIX environments as well as Windows. It even includes support for Cisco-specific NetFlow features and sFlow as well! ntop is a particularly common choice as one of the more well-known open-source offerings for NetFlow collection and analysis.
Key Features:
- Packet Capture Capture data packets from a network even if you are not physically at the location of the network, allowing you to centralize monitoring and analysis of network traffic across multiple sites or networks.
- Traffic Recording n2disk tool records network traffic at speeds of up to 100 Gbps without any loss. It stores the captured data in PCAP file format, which includes nanosecond-level timestamps for precise timing. This allows for accurate analysis of network traffic down to the smallest intervals.
- Network Probe Offers data export and collection capabilities using NetFlow v5/v9/IPFIX protocols. These protocols help monitor and analyze network traffic by collecting data on IP flows. Using this data, you can improve network security and performance.
Why do we recommend it?
ntop comes with wide-ranging features like packet capture, traffic recording, network probe, and traffic analysis. It also integrates with leading tools like PagerDuty to provide high levels of flexibility.
ntop is somewhat unique in that the interface is purely web based and makes it a lot easier to navigate and manipulate via several client machines and, what's more, there's even a github variant for macOS support.
Who is it recommended for?
Free for educational and not-for-profit organizations. It also works well for small and medium organizations.
Pros:
- Open-source project with full transparency
- Free version available alongside the enterprise version
- Special licensing options for nonprofits and educational institutions
Cons:
- Easy-to-use interface, but could be improved upon
Download link: http://www.ntop.org/get-started/download/
4. EHNT
‘Extreme Happy NetFlow Tool,' or EHNT, despite its rather quirky name is a simple and solid offering. It's just about as barebones as you can get, running with a simple terminal interface that basically just grabs NetFlow data and parses it into the most basic humanly-readable format that it can manage.
Key Features:
- Human-Readable Format Converts hard-to-read NetFlow data into human-readable format, parsing network data for better understanding.
- Report Generation Generates reports in many formats and multiple modes, making it a versatile choice across different scenarios. You can even generate these reports over various intervals, running from once a minute to once a day.
- Simple to Use A highlight of EHNT is its simple terminal interface. You can see the way it captures a packet and converts the contents into a human-readable format. No complex syntax or coding knowledge is necessary to use this tool.
Why do we recommend it?
EHNT is a useful tool for converting Netflow data streams to something more human-readable. It also operates in several modes and generates reports for many purposes.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for network administrators who use operating routers for exporting NetFlow packets.
Pros:
- Syntax is easy to learn
- Can provide scheduled reports as often as every 60 seconds
- Is easier to use than other command line Netflow analyzers
Cons:
- Solely a command line tool, no GUI available
- Only supports Netflow 5
Download link: http://ehnt.sourceforge.net/
5. Flow-tools
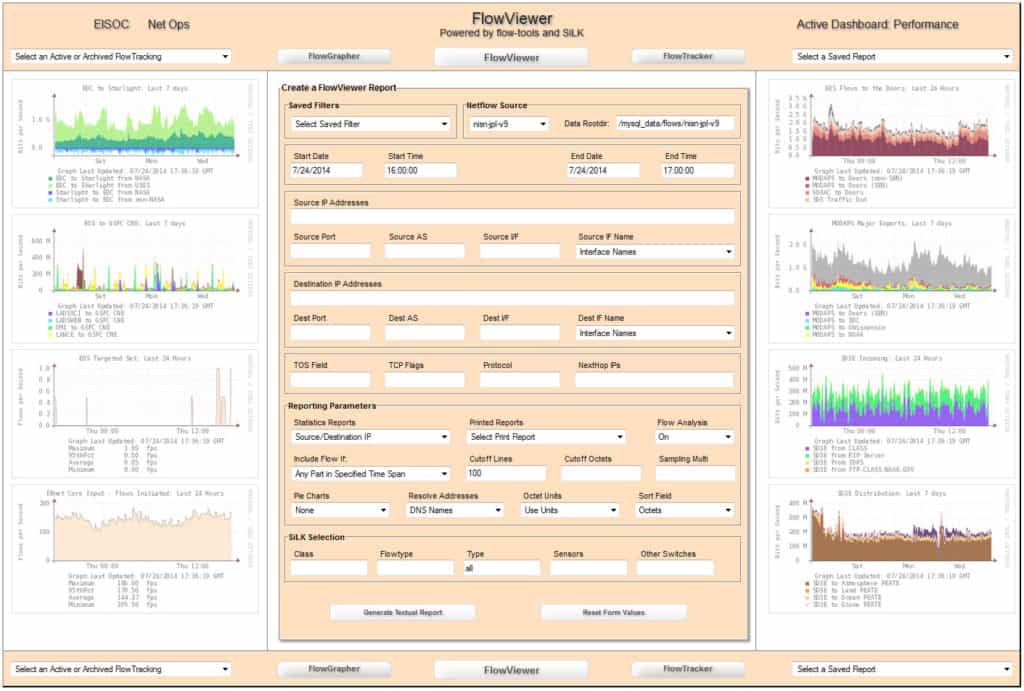
Flow-tools, often paired with FlowViewer which is pictured above, is another pretty straightforward and simple open-source NetFlow analysis program.
Key Features:
- Flexible Deployment Can be deployed on a single server or can be distributed across multiple servers to support large deployments. Furthermore, you can decide which programs to install depending on your objective.
- High Customization Customize to meet your specific needs, and comes with an API for custom applications. Also supports NetFlow export versions 1, 5, 7, and 6. A Perl and Python interface is also included.
- Multiple Use Cases Used across multiple use cases, and comes with 17 distinct tools, with each tool acting on a specific aspect of the NetFlow data.
Why do we recommend it?
Flow-tools is a highly flexible tool, as you can select what programs to install to meet specific objectives. Such versatility opens up a lot of choices to decide what you want to do with the NetFlow data.
Coupled with FlowViewer, another open-source offering that works specifically with Flow-tools, it becomes another web-interface based option for easy perusal and visualization of NetFlow statistics.
Who is it recommended for?
Highly recommended for network administrators and network engineers who have to make sense of NetFlow data and use it for troubleshooting and enhancing efficiency.
Pros:
- Complete toolset for Netflow data collection and processing
- Creates custom reports based on collected data
- Maintains a small but active team
Cons:
- Steeper learning curve than similar tools
Download link:https://manpages.ubuntu.com/manpages/focal/man1/flow-tools.1.html
6. BPFT
BPFT is more of an add on than its own standalone offering. It adds onto the libpcap library and uses, as the name implies, the Berkeley Packet Filter (BPF) mechanism for capturing IP traffic to perform NetFlow analysis.
Key Features:
- Captures IP Traffic Works on top of libpcap and uses the Berkeley Filter Traffic mechanism for capturing IP traffic for further analysis, storing all collected information into a single binary file in a compact form via cron.
- Supports Add-Ons Flexibility to integrate with tools like MySQL using add-ons, and many scripts are also available to build HTML files that can write daily and monthly statistics.
- Backup and Retrieval Saves backups from memory to disk file using cron, and this is restored when the daemon starts again, also retrieves information based on different criteria, and use it to get actual information from the daemon through a socket.
Why do we recommend it?
BPFT is a powerful tool for intrusion detection analysis. Specifically, it reduces large file packet captures to a small set of results.
Who is it recommended for?
Though it can be used both by admin and non-admin users, a certain amount of technical knowledge about CLI and filters is needed.
Pros:
- Tested specifically for Free/Open BSD
- Supports saving backups to local disk
- Detailed tool, logs and stores all network information by default
Cons:
- Only runs on Unix systems
Download link: http://bpft4.sourceforge.net/
7. Panoptis
Panoptis is another open-source project for which development has tapered off but still a useful one for some needs. This particular program uses NetFlow data and analysis in an attempt to attempt to detect and, more importantly, stop DDoS style attacks on networks.
Key Features:
- Prevents DoS and DDoS Attacks Uses NetFlow data to detect impending DoS and DDoS attacks, it then processes this data in real time and takes an automated central response that requires no intervention from network administrators.
- Sends Notifications If an imminent attack is detected, the mail.py script is used to email administrators about the attack. It also connects to others mentioned in the configuration to notify them.
- Router-Centric Takes a router-centric approach, meaning the input comes from the routers, ensuring that the data is authentic.
Why do we recommend it?
Panoptis is a handy tool for detecting and blocking DoS and DDoS attacks. It processes Netflow data in real time to generate automated responses. While work on the project may resume in the future, for now it's dead in the water, meaning it may or may not have much to offer for you.
Who is it recommended for?
It can be useful for network administrators who want a tool that will automatically detect DDoS attacks.
Pros:
- Leverages Netflow data to detect and prevent DDoS attacks
- Built to provide data for Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS)
- Well-documented, easy to deploy
Cons:
- No longer being supported, last update was in 2014
Download link: http://panoptis.sourceforge.net/
Conclusion
Many of these tools are more than sufficient for many network environments, but there are cases where they may fall short.
Be sure to assess each tool firsthand, and consider your network and the importance of each aspect of tracking and analysis. Admins who are running non-critical systems or have a smaller environment that isn't as easily crippled financially by an outage may find little issue here. But for those overseeing multiple data centers, or huge customer-facing servers may hesitate to put their well-being in the hands of the options above.
Individuals dealing with heavier or more strict and rigid environments would be best suited to check out some of the paid options, which tend to offer free trials and demos, and can more than justify their cost.
Open-Source Netflow Analyzers FAQs
What is the Netflow protocol?
The Netflow protocol is a network protocol developed by Cisco that allows network devices, such as routers and switches, to collect and export information about network traffic flows. This information can include details about source and destination IP addresses, packet counts and sizes, and protocols used.
What are some popular Netflow Analyzers?
Some popular Netflow Analyzers include:
- SolarWinds NetFlow Traffic Analyzer
- Paessler PRTG Network Monitor
- ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer
- Scrutinizer NetFlow and sFlow Analyzer
- Kentik Detect
What information can I gather using a Netflow Analyzer?
A Netflow Analyzer can provide detailed information about network traffic, including:
- Top talkers and protocols
- Traffic volumes and bandwidth usage
- Applications and hosts consuming network resources
- Network usage patterns and trends
- Security threats and anomalies
How does a Netflow Analyzer work?
A Netflow Analyzer works by collecting flow data from network devices that support the Netflow protocol, such as routers and switches. It then processes and analyzes this data to provide insights into network traffic patterns and usage. Some Netflow Analyzers can also perform additional functions, such as monitoring network performance and identifying security threats.
What are some common errors I might encounter when using a Netflow Analyzer?
Some common errors you might encounter when using a Netflow Analyzer include:
- Configuration errors that prevent the Netflow data from being properly collected or analyzed
- Network connectivity issues that prevent the Netflow data from being transmitted or received
- Incorrect or incomplete data that can result in inaccurate or misleading analysis
- Insufficient hardware resources, such as CPU or memory, that can impact the performance of the Netflow Analyzer.
Related Post: Best Penetration Testing Tools