A couple of years ago, I was asked to consult on a project: an organization was getting a lot of bandwidth from their ISP but they couldn’t figure out why connecting to the Internet was still very slow.
After spending a few days on the client’s site, I eventually discovered that the source of their problem was a faulty router interface that was dropping more than half of the bandwidth they were receiving from their ISP.
Here is our list of the best bandwidth monitoring tools:
- SolarWinds NetFlow Traffic Analyzer – FREE TRIAL A bandwidth monitoring system that can be used for live monitoring and also historical traffic pattern analysis. Installs on Windows Server. Access the 30-day free trial.
- Paessler PRTG Bandwidth Monitoring Tool – FREE TRIAL Part of a wider package of system monitoring tools, this service offers a range of sensors to supervise traffic flows. Installs on Windows Server. Get a 30-day free trial.
- ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer – FREE TRIAL A useful tool for detecting traffic problems, identifying bandwidth hogs and peak traffic times. Available for Windows Server and Linux. Get a 30-day free trial.
- Site24x7 Network Traffic Monitoring – FREE TRIAL This cloud platform of monitoring system provides plans that include full stack monitoring tools that makes it an ideal service for data center monitoring. Get a 30-day free trial.
- Noction Flow Analyzer This on-premises monitoring system delivers network traffic monitoring for live activity and a capacity planning analyzer based on historical traffic data. Runs on Linux.
- nTop-Ng Available in free and paid versions, this network traffic analyzer has a simple and unsophisticated interface. Available for Windows, Linux, macOS, Raspberry Pi, and Unix.
- Cacti A free, open source network data analyzer templates for network topology mapping. Installs on Windows and Linux.
- BandwidthD A free, open source network bandwidth analyzer that has become a little out of date. Installs on Linux.
Why did I tell that story? Well, if that organization had been monitoring the bandwidth on their network, perhaps I would not have stayed that long looking for the problem.
In fact, maybe they would not have needed to call me in to find the problem (not like I’m complaining).
The question then arises: Why do we even need to monitor the bandwidth on a network?
There are several reasons some of which are as follows:
- Troubleshoot Network Performance:
Network Bandwidth monitoring can help you identify performance issues on a network like in the example I gave above. For example, by monitoring network bandwidth, you may find out that a particular computer on the network is consuming (hogging) so much bandwidth which may be an indication of a worm or virus. In other cases, you'll find that analyzing Wifi Access Points and connected Clients that are using it will help you determine who is potentially abusing it. - Network Capacity Planning:
By monitoring network bandwidth, you are able to plan ahead regarding the bandwidth capacity that your network requires. For example, when you start out your network, you may have a few hundred devices and require a hypothetical 100 Mbps of bandwidth. As the network grows in size, you may find out (through monitoring) that the 100 Mbps is being maxed out at peak periods and should be upgraded. - Monitoring Agreed-Upon Bandwidth:
When you purchase bandwidth (e.g. Internet) from Internet Service Providers (ISPs), they guarantee that the speed will be at a certain level (usually expressed in Megabits per second, Mbps). By monitoring network bandwidth, you can determine if your ISP is really giving you the bandwidth that was agreed upon or if they are failing on their Service Level Agreement (SLA).
As the Internet evolves and the rise of faster and larger handheld devices and tablets become the norm in the workplace, we strongly believe that knowing who and what devices are consuming the most data and pipeline in your infrastructure in order to better control it and plan for capacity.
As the name implies, a Network Bandwidth Monitoring tool lets you keep an eye on bandwidth and traffic usage on the network. These tools will usually be able to report on single nodes (e.g. traffic usage by a single computer) or on interfaces (e.g. FastEthernet0/0 interface on a router).
Some of these tools will be able to present this information in graphs and also sort devices (or IP addresses) based on top bandwidth “consumers”.
To get this traffic usage information, several methods can be employed including packet capturing, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) or NetFlow (or some other flow related technology).
The Best Bandwidth Monitoring Tools
Some of these tools are standalone network bandwidth monitoring tools while others are all-in-one network monitoring solution that include bandwidth monitoring amongst other features.
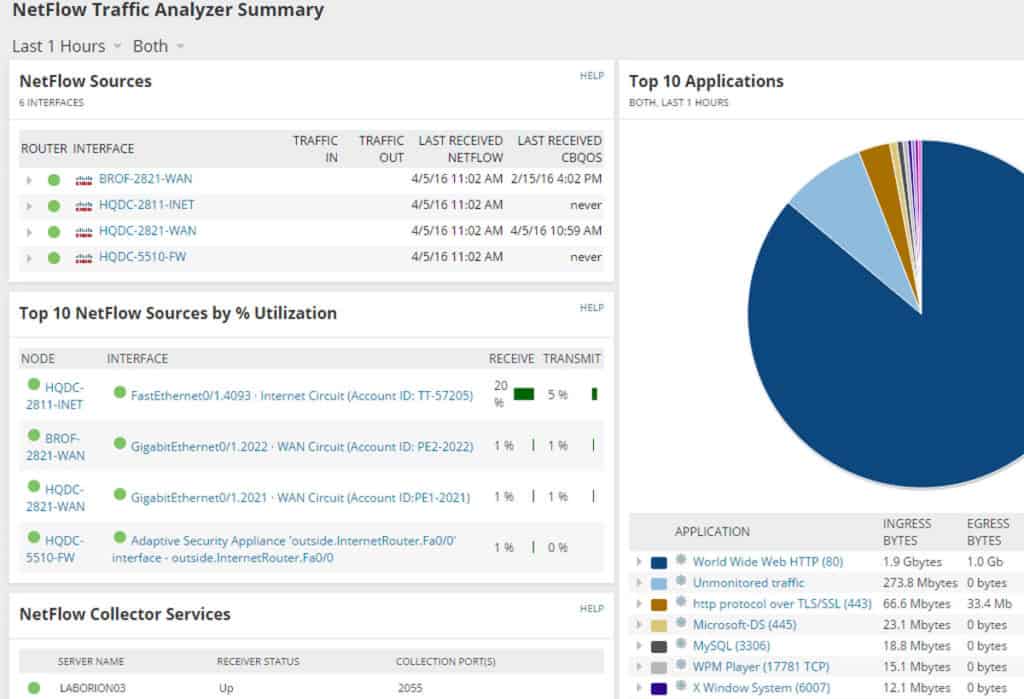
1. SolarWinds NetFlow Traffic Analyzer – FREE TRIAL
The NetFlow Traffic Analyzer (NTA) integrates with the SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM) and provides information about the bandwidth and traffic usage on a network at a very granular level.
It is able to tell you the amount of bandwidth used by an IP address, application or protocol. It also has the ability to show the “Top Talkers” on a network which is very helpful for troubleshooting purposes.
The SolarWinds NTA has reporting capabilities and can be used for Network Traffic Forensics (comb through data over several periods to discover issues).
Pros:
- Supports multiple protocols like NetFlow, great for monitoring Cisco equipment
- Both tools work well alongside each other to help view traffic patterns and bandwidth usage
- Easy to use interface automatically highlights bandwidth hogs and other network traffic outliers
- Scales well, designed for large enterprise networks
- Can view traffic on a per-hop basis, allowing for granular traffic analysis
Cons:
- Built for enterprise use, not designed for small home networks
You can try a fully functional SolarWinds Network Traffic Analyzer for 30 days after which you will require a license starting at $1875 for 100 elements.
Keep in mind that since NTA requires SolarWinds NPM to function, you must also account for the separate license cost of the NPM. Get started with a 30-day free trial.
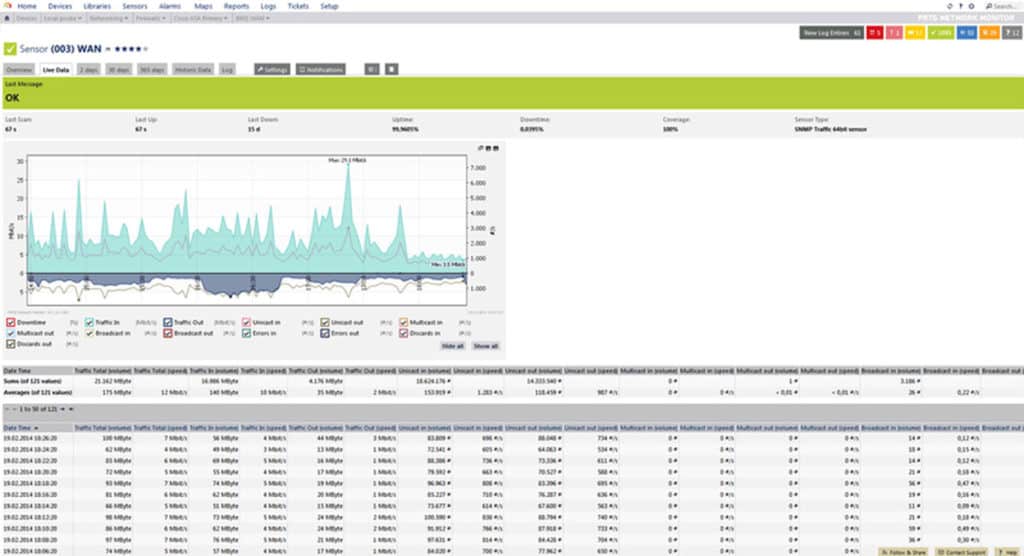
2. PRTG Network Monitor – FREE TRIAL
PRTG Network Monitor is a full blown, all-in-one monitoring solution with a lot of features including performance monitoring, server and application monitoring, virtual machine monitoring and also includes bandwidth monitoring.
To provide information about bandwidth and traffic usage, PRTG Network Monitor can use a variety of methods including SNMP, in-built Packet Sniffing and NetFlow. This information can be displayed in graphs and also exported in reports. We written up a thorough and exhaustive PRTG Review and Setup Guide for those who are interested in a more in-depth look.
PRTG Network Monitor is a Windows-based tool that comes in two editions: Freeware edition (for monitoring up to 100 sensors) and Commercial Edition (when you want to monitor more than 100 sensors) which starts at $1600 for 500 sensors.
Pros:
- Drag and drop editor makes it easy to build custom views and reports
- Supports a wide range of alert mediums such as SMS, email, and third-party integrations into platforms like Slack
- Supports a freeware version
Cons:
- Is a very comprehensive platform with many features and moving parts that require time to learn
Note: There is also a 30-day free trial that allows you to monitor unlimited sensors after which it falls back to default 100 sensor limit.
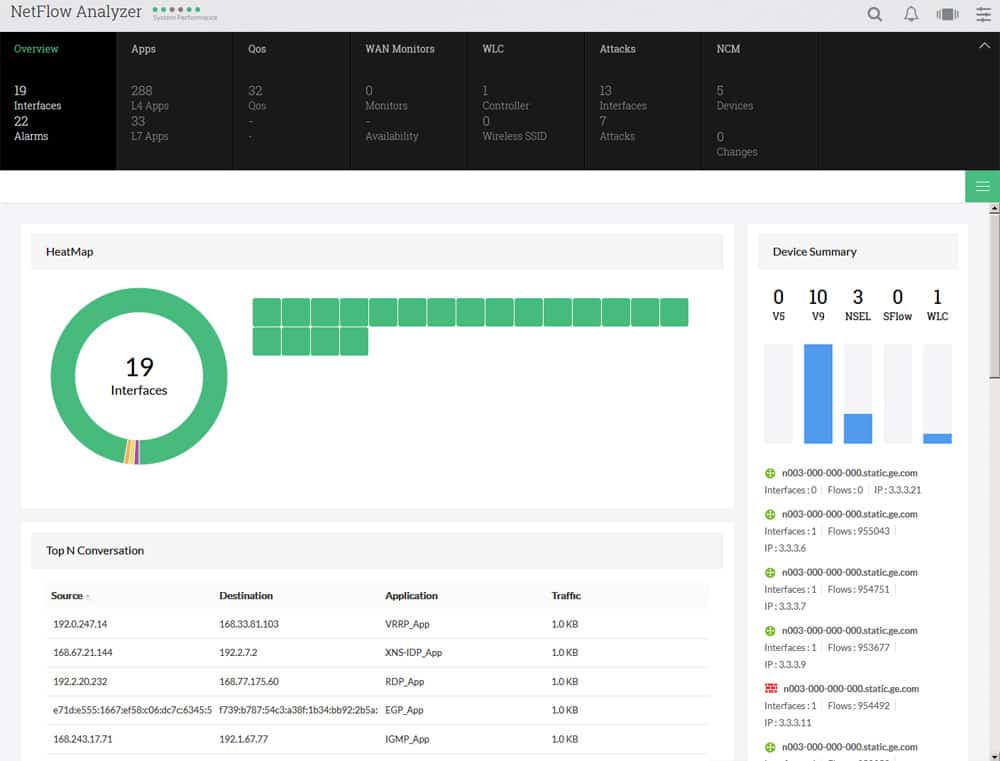
3. ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer – FREE TRIAL
ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer traffic analysis and monitoring tool for monitoring flow packets, including Netflow, Sflow, IPFix and others is a great choice finding and determining the cause of your bottlenecks. You can analyze bandwidth patterns per interface and drill down into which protocol, IP address and/or application is causing the issues with your network connection or network overhead.
On top of the basic functionality of traffic analysis and monitoring, you'll have the ability to create detailed reports and precisely estimate for future growth and bill as necessary if you are providing SLA's or ISP services.
Pros:
- Supports multiple protocols like NetFlow, great for monitoring Cisco equipment
- Both tools work well alongside each other to help view traffic patterns and bandwidth usage
- Easy to use interface automatically highlights bandwidth hogs and other network traffic outliers
- Scale well, designed for large enterprise networks
- Can view traffic on a per-hop basis, allowing for granular traffic analysis
Cons:
- Built for enterprise use, not designed for small home networks
Get started with a 30-day free trial.
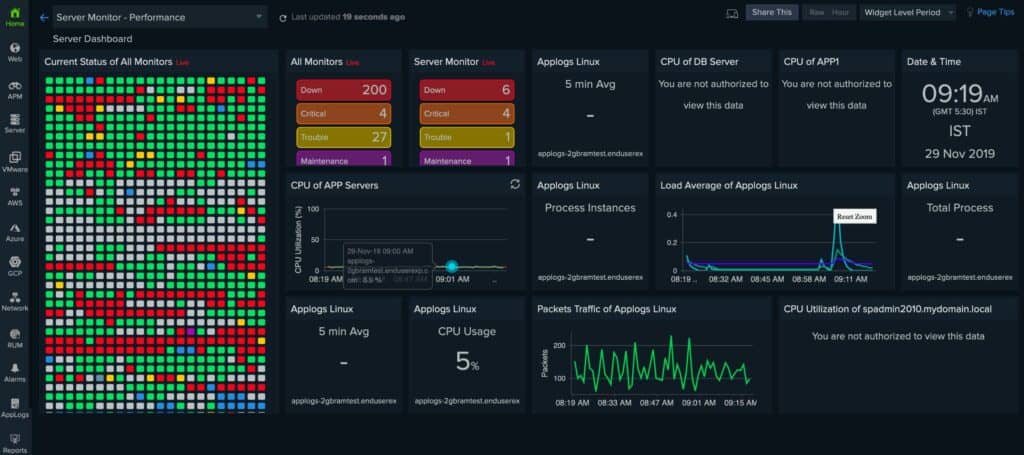
4. Site24x7 Network Traffic Monitoring – FREE TRIAL
Site24x7 Network Traffic Monitoring is part of a cloud platform of system monitoring services. This unit reaches out to your network and communicates with network devices by using NetFlow, J-Flow, sFlow, CFlow, IPFIX, NetStream, and AppFlow to extract traffic statistics. The traffic system pairs with a device monitor to create an inventory and map of the network.
Although this system can be used to show live traffic data, its greatest value lies in a long-term perspective for capacity planning and traffic shaping measures. The system displays link throughput and capacity. It is also possible to use the tool to check end-to-end paths through the network.
The console for the Site24x7 system is hosted in the cloud and in can be accessed from anywhere through any standard Web browser. The screens for the network traffic monitor and all of the other monitors on the platform can be customized. The traffic monitor can be expanded by integrations, which give the tool extra power for monitoring a specific product. However, you are only allowed one integration for free with the base package for this tool.
Pros:
- Measure VoIP transmission quality
- Provides analysis for traffic shaping
- Link analysis and path testing
Cons:
- No on-premises version
The Network Traffic Monitoring unit of Site24x7 is part of the Infrastructure package. This includes network performance monitoring, server monitoring, and an APM as well as the traffic monitor. The package is available for a 30-day free trial.
5. Noction Flow Analyzer
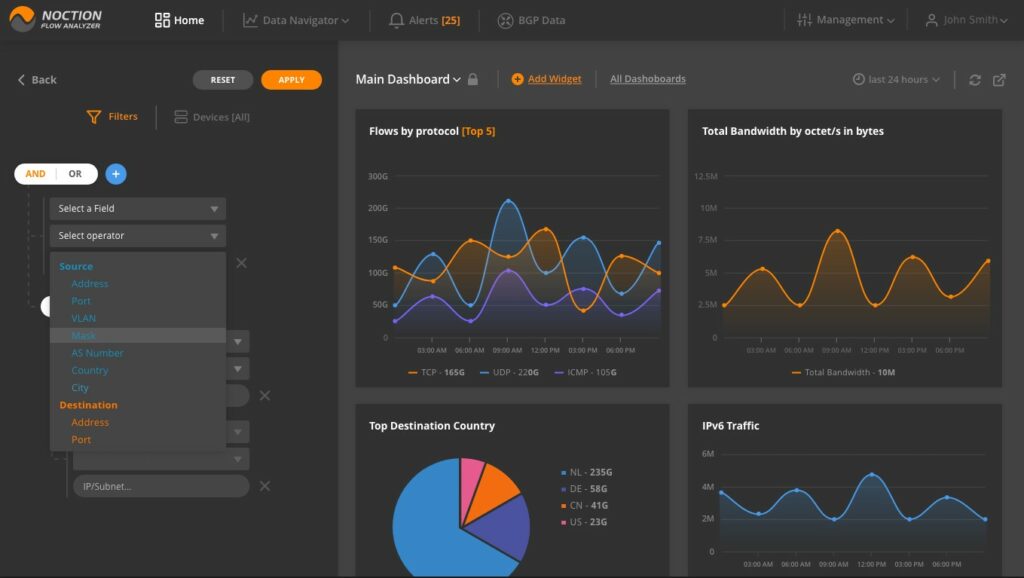
Noction Flow Analyzer offers live network performance monitoring, network traffic analysis, and a capacity planning capabilities. The live traffic monitor collects data from switches and routers using the NetFlow, IPFIX, sFlow, NetStream, and J-Flow protocols. This range of communication services enables the Flow Analyzer to operate in multi-vendor environments.
The traffic monitor consolidates all of the statistics that it draws from the network devices that it encounters. This enables it to present an overview of all network traffic in the dashboard. That data can then be explored through drill-down views.
As well as displaying the traffic data, Noction Flow Analyzer stores it. That stored data can be recalled for detailed analysis. So, you can work with the same data immediately and retrospectively to get a full understanding of the traffic patterns on your network.
Pros:
- Does an excellent job at creating insights and statistics from network information gathered
- Best suited for Linux environments
- Offers Juniper-specific templates
Cons:
- Site24x7 is a feature dense platform that can take time to fully learn all of its features and customization options
Noction charges for the Flow Analyzer software by subscription on monthly and yearly tariffs. The system is an on-premises package that was written for Linux. It will run on Ubuntu, CentOS, and RHEL. You can get a free trial to test Noction Flow Analyzer.
Learn more about this tool here. Register for a download.
6. ntopng
My first experience with ntopng was with a client where I had to determine why Internet access was slow at certain times. The client was using pfSense as their edge device and ntopng was installed as a default package. Using ntopng, I was able to discover that one of the client’s servers had been hacked and was consuming so much bandwidth (probably being used as a streaming server) that the client was even maxing out the bandwidth provided by their ISP.
ntopng has a very simple web interface from which you can view network bandwidth/traffic usage information. ntopng can sort network traffic based on different options such as IP addresses, protocols, and ports. I especially like the “Top X talkers/listeners” feature provided by ntopng because it can let you know what device is currently hogging all the bandwidth on the network. ntopng also has reporting capability for what it monitors.
Pros:
- Open-source project with full transparency
- Free version available alongside the enterprise version
- Special licensing options for nonprofits and educational institutions
Cons:
- User interface is easy to use, but could be improved upon
ntopng can be installed & used to monitor on both Unix and Windows operating systems. It comes in two editions: the Community edition which is free and the Professional edition which comes at a cost (149 Euros). You can find more information about ntopng here.
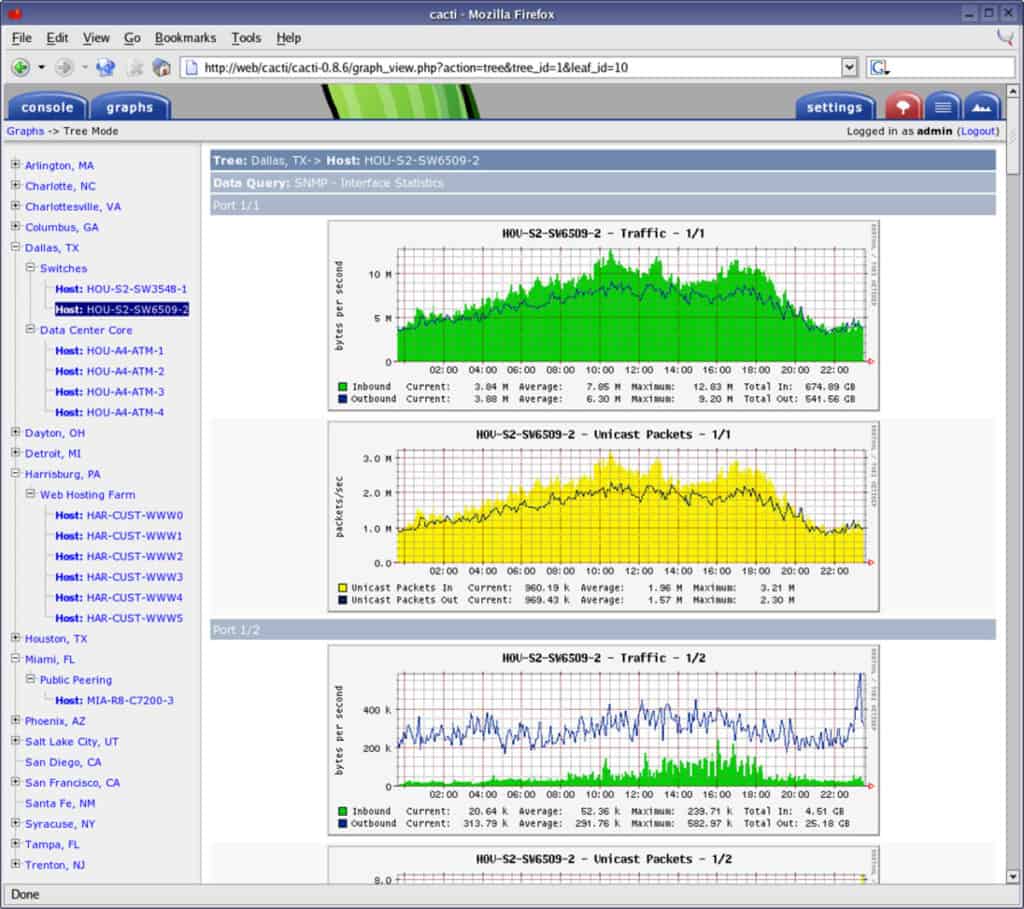
7. Cacti
Cacti is an open-source network monitoring tool whose greatest strength lies in its graphing capability. It works by polling devices (mostly through SNMP) and presenting the polled data in graphs displayed through a web interface. Since it uses SNMP, one of the things you can graph is the network bandwidth usage on an interface, thereby making Cacti a valuable tool for Network Bandwidth Monitoring. If it doesn't suite your needs, you can find a Cacti Alternative here.
Pros:
- Highly customizable monitor with a focus on data visualization
- Large dedicated community of over 20,000 members
- Simple interface
- Ideal for researchers looking for more flexibility in their data collection
Cons:
- Has a steeper learning curve than competing product
Cacti can be installed on either Unix or Windows OS and are available to download for free here.
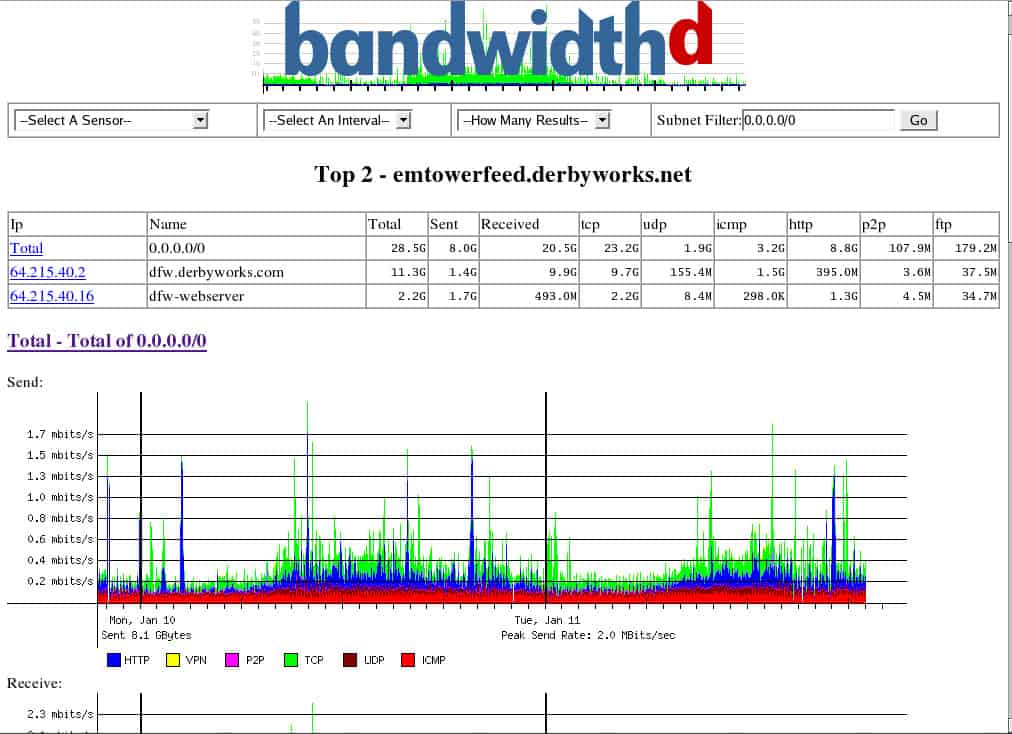
8. BandwidthD
BandwidthD is another open-source solution for monitoring your traffic and network, but be aware, it has not been updated since 2013. Many admins are still using this software to understand which protocols and sources are using the highest amount of bandwidth in their networks.
You'll need to understand how to setup some manual configurations and it also requires some dependencies, including winpcap or libpcap (for linux/unix users) in order to collect data and such.
Pros:
- Open-source and transparent project
- Decent option for Linux environments
- Native graphical reporting
- Completely free
Cons:
- Slightly out of date when compared to competing tools
- Better suited for smaller networks
Overall though, its a free utility and has potential, although you should not expect any support of any kind with this software.
Conclusion
Being able to monitor bandwidth and traffic usage on a network can be very beneficial because you can use it to assess network performance issues, plan network capacity and also verify SLAs.
Looking at the tools we have discussed in this article, if you want to quickly set up a bandwidth monitoring tool, you may want to go for the SolarWinds Real-Time Bandwidth Monitor – It is by far the easiest and cheapest solution to get you started here and now.
If you are looking for a more robust solution that can give granular information, consider PRTG Network Monitor or SolarWinds NetFlow Traffic Analyzer (if cost is not a problem). If you are more interested in graphs, then Cacti may be the best tool to use.
We suggest your Grab the Latest FREE Version of SolarWinds Free Tool at NO-COST and get started Immediately.
Direct download Link can be found here: https://www.solarwinds.com/free-tools/network-analyzer-bandwidth-monitoring-bundle/registration
Bandwidth Monitoring Tools & Software FAQs
What are some common tools used for bandwidth monitoring?
There are many tools available for bandwidth monitoring, ranging from simple command-line utilities to complex network monitoring systems. Some common tools include NetFlow, SNMP, Wireshark, PRTG, and SolarWinds.
How does bandwidth monitoring work?
Bandwidth monitoring works by analyzing network traffic data to measure the amount of data being transmitted over the network. This data can be collected using various monitoring tools such as network probes, flow analyzers, and packet sniffers. Once the data is collected, it can be analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies in network traffic.
What are some best practices for bandwidth monitoring?
Some best practices for bandwidth monitoring include setting clear goals and objectives for monitoring, selecting the right tools for the job, monitoring network traffic at various points in the network, establishing baseline performance metrics, and regularly reviewing and analyzing monitoring data to identify trends and patterns.
What are some common metrics used in bandwidth monitoring?
Some common metrics used in bandwidth monitoring include bandwidth utilization, packet loss, latency, jitter, and throughput. These metrics can help you identify performance issues and optimize network performance.
How can I use bandwidth monitoring to optimize network performance?
Bandwidth monitoring can help you optimize network performance by identifying bottlenecks and congestion points, tracking down the source of performance problems, and providing insights into network traffic patterns. By analyzing monitoring data, you can make informed decisions about network configuration, bandwidth allocation, and traffic management to improve network performance.