SNMP Is used in almost Every networking device and Computer/Server in your IT Infrastructure – We've gone through many other monitoring protocols, including WMI Monitoring tools, IP Monitoring tools, and Network Diagnostic Tools in the past, but this article will highlight SNMP Scanning Software and tools for your network.
Here is our list of the best SNMP Scanning Tools:
- ManageEngine OpManager – EDITOR'S CHOICE This network monitoring system uses SNMP to discover and communicate with network devices. The tool monitors servers as well and it is available for Windows Server and Linux. Download the 30-day free trial.
- ManageEngine Network Scanner – FREE TRIAL Part of the OpUtils package, this tool is also offered individually for free. It aids in the discovery of devices as part of an IP address management strategy. Available for Windows Server and Linux. Download the 30-day free trial.
- Site24x7 – FREE TRIAL A cloud-based package of tools that includes an SNMP-based network device monitor and an MIB interpreter that creates a hardware inventory and a network topology map. Start a 30-day free trial.
- SolarWinds SNMP Scanner Part of the Network Performance Monitor, which uses SNMP for regular system checks, this scanner tool performs on-demand SNMP sweeps. Runs on Windows Server.
- Mitec Network Scanner This versatile network scanning tool includes a variety of system tests and discovery utilities including an SNMP manager. Installs on Windows and Windows Server.
- Adrem Software SNMP Scanner This free tool is part of the NetCrunch suite of network management utilities. Installs on windows.
- SNMP Device Network Management Τhis affordable tool from SoftInventive Lab performs SNMP sweeps on demand or on a schedule. Installs on Windows.
- NetScan Tools SNMP – Core This tool performs SNMP data gathering on demand. Runs on Windows.
- Secure Bytes SNMP Scanner This SNMP scanner is particularly focused on identifying the community string (password) used on the network for SNMP access. Available for Windows and Windows Server.
What is SNMP?
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a scanning technology that is used as a Network Discovery tool and data gatherer. Many network scanning tools use SNMP as a means to collect valuable information about the current state of devices on the immediate network.
Things like printers, computers, servers, and even some versions of software are detectable from SNMP capable applications, so it is very useful and effective in administering and managing your company’s resources.
There are other benefits to it as well, such as finding out serial numbers of your hardware, and even warranty stats and toner and ink levels in printers around the office.
We want to look at some of the products that you can use to try and get your network in tip top shape, with no unknown quantities being in the mix.
A known quantity on a network is far better than anything that will take you by surprise much later, such as a rogue device like a small computer or network device.
The Best SNMP Scanner Tools and Software
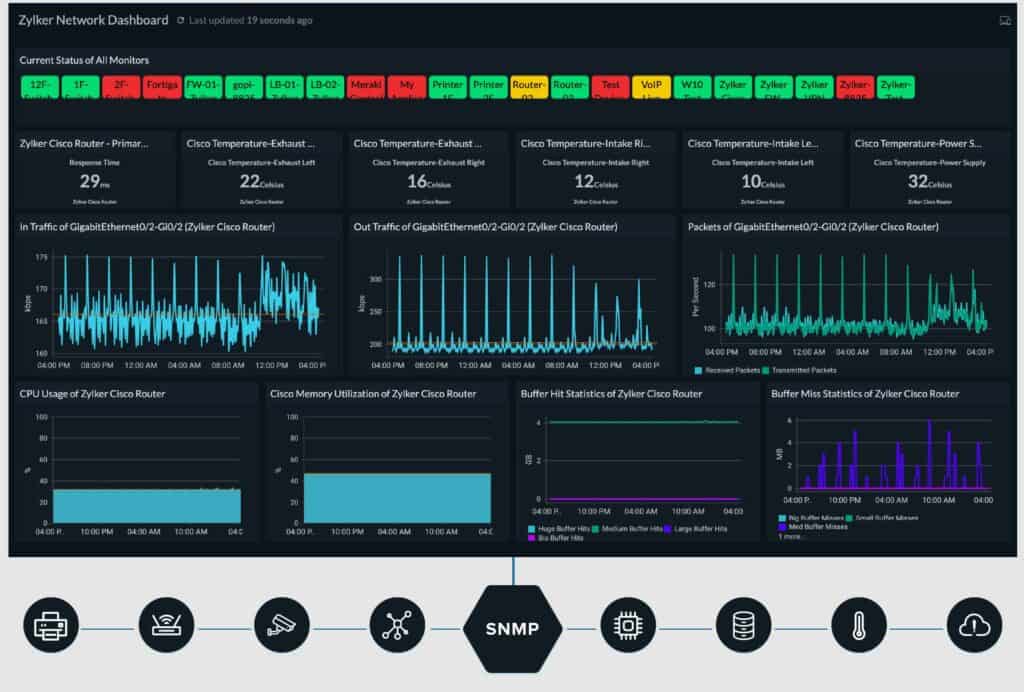
1. ManageEngine OpManager – FREE TRIAL
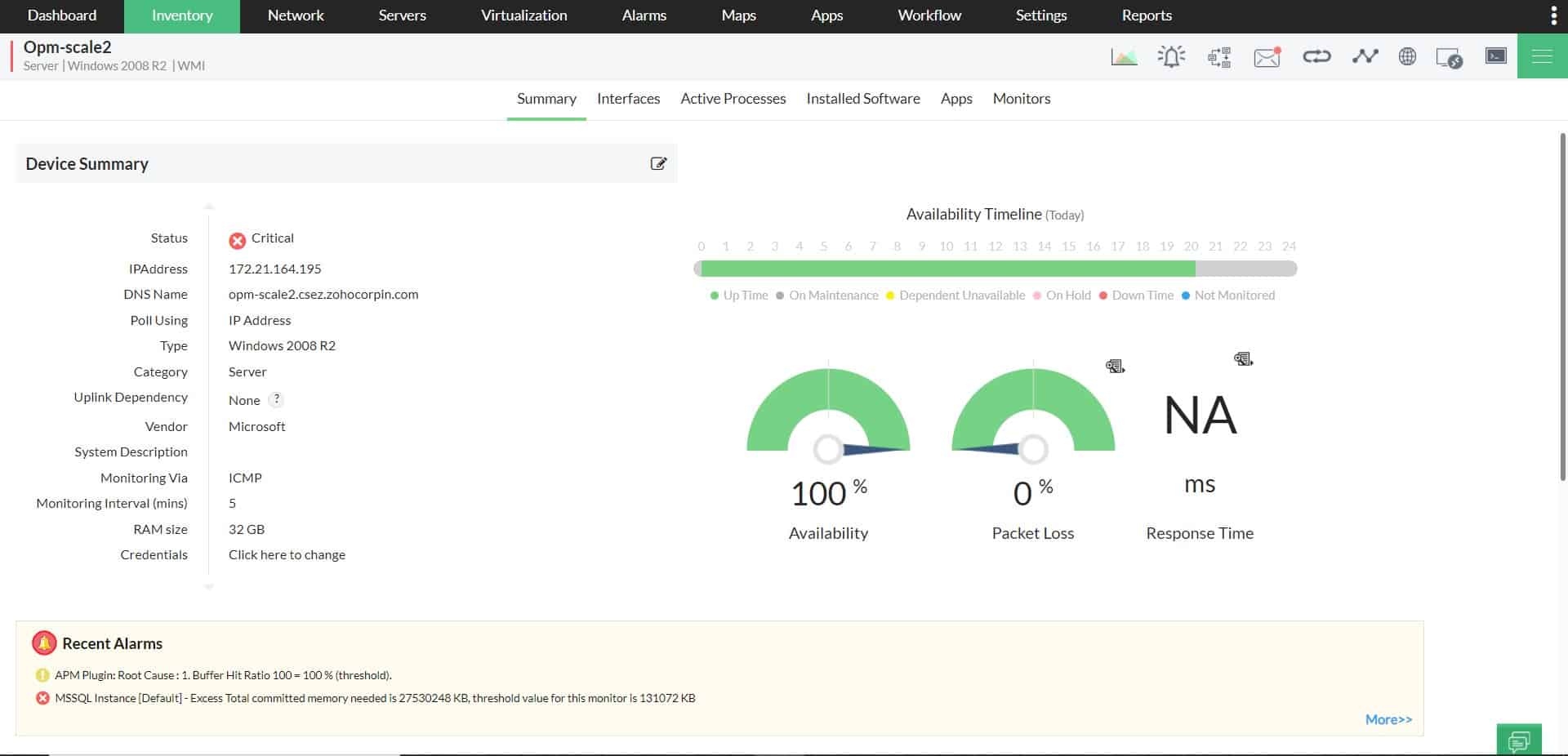
ManageEngine OpManager monitors networks and servers. The network monitoring part of the package is heavily reliant on SNMP for its functions.
The OpManager network monitor starts its service life with an initial SNMP request poll. The OpManager system acts as the SNMP Manager and receives back MIBs from all device agents in response to its request broadcast. The service compiles all of the MIB information for a performance report page for each device.
The device report offers live performance statistics. The OpManager module repeatedly sends out status requests, refreshing the device performance screen with each cycle and compiling time-series graphs for selected metrics.
The initial performance screen gives the vital metrics for that device and you can select which pieces of information appear on that screen. However, a back screen provides all data returned in the MIB.
The OpManager dashboard also displays status alerts, which are derived from any Trap messages sent back by agents. The settings of OpManager allow you to specify an email account or mobile number to which the service can forward alerts as email or SMS notifications.
Other features in the OpManager package are server monitoring, Active directory monitoring, web and email server monitoring, VLAN monitoring, and virtualization monitoring. All of the services and software that the system monitors are measured by performance thresholds that will generate alerts if crossed.
Pros:
- Can automatically produce metrics such as unused addresses, IP conflicts, and available IP addresses based on subnet
- Leverages both ping and SNMP protocol to detect device uptime and performance issues
- Build an automatic network topology map updated in real-time
- Has log collection capabilities, allowing it to provide much more detailed information than other tools
Cons:
- OpManager is a tool designed for IT professionals, non-technical users may find the platform overwhelming
ManageEngine OpManager is a software package and it installs on Windows Server and Linux. There are four editions of the package.
- Free for up to three devices — $0
- Standard starting at a price to monitor 10 devices — $245
- Professional starting at a price to monitor 10 devices — $345
- Enterprise starting at a price to monitor 250 devices — $11,545
ManageEngine OpManager is available for a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
ManageEngine OpManager is our top pick for an SNMP scanning tool because it offers powerful, intuitive features that simplify network monitoring and management. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is widely used for gathering performance data and managing network devices. OpManager excels in its ability to efficiently discover and monitor SNMP-enabled devices across large and complex networks. The tool’s automatic device discovery feature scans the entire network, identifying SNMP-enabled devices such as routers, switches, and printers, and adds them to the monitoring console for real-time tracking. OpManager's customizable SNMP polling allows users to set specific thresholds for different network parameters like CPU usage, memory usage, bandwidth, and device health. This ensures that administrators can focus on critical metrics that directly affect network performance, while the system alerts them when these thresholds are breached. Its detailed reports and visualization tools, including network topology maps, allow users to gain comprehensive insights into their network’s health and performance. OpManager can manage SNMP devices from various manufacturers without compatibility issues. The tool also integrates seamlessly with other IT management software, providing a complete solution for network administrators. Overall, ManageEngine OpManager’s robust SNMP scanning, coupled with its scalability and ease of use, makes it our top choice for SNMP-based network monitoring.
Download: Get a 30-day FREE Trial
Official Site: https://www.manageengine.com/network-monitoring/download.html
OS: Windows Server, Linux, AWS, and Azure
2. ManageEngine Network Scanner – FREE TRIAL
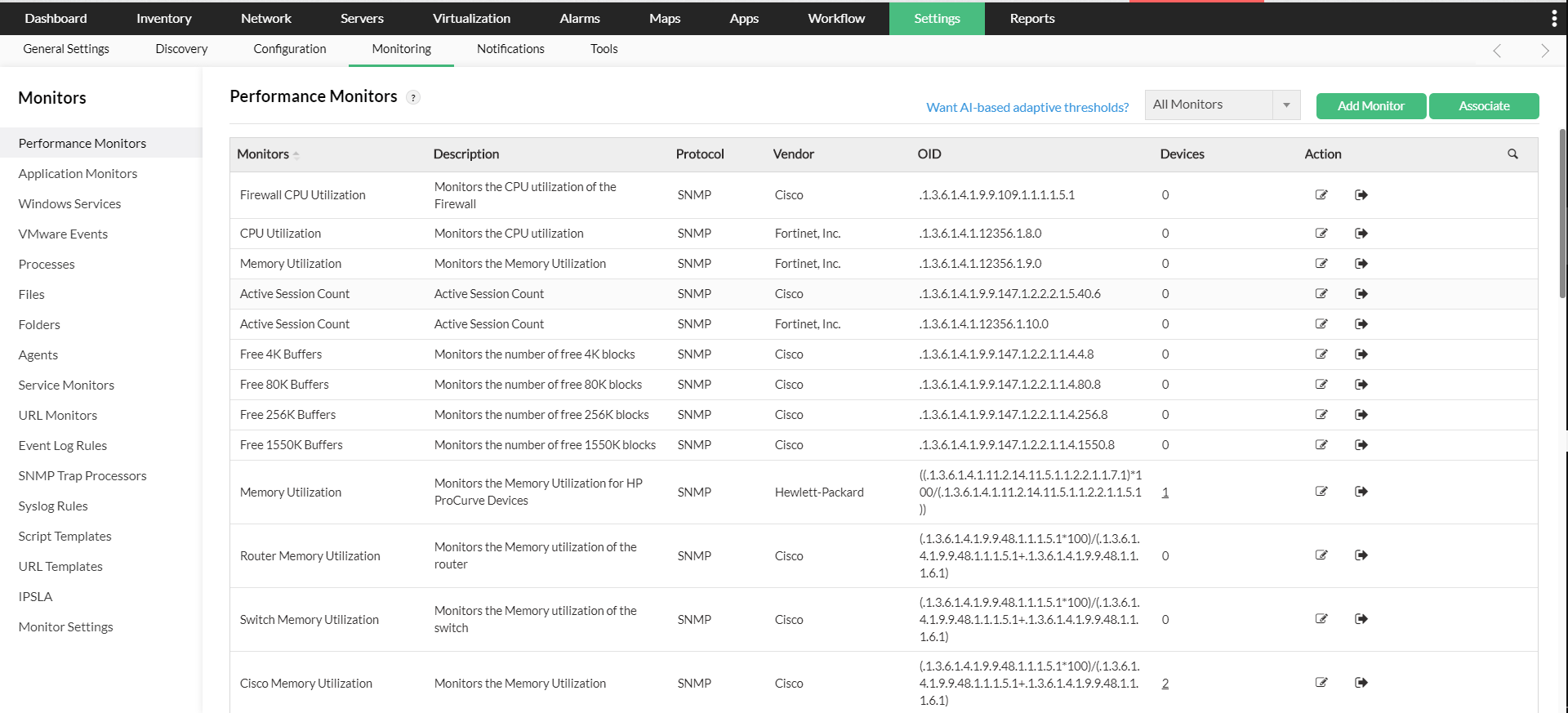
ManageEngine OpUtils offers a free range of network utilities that help you to pin scan and SNMP scan for devices on your network. SNMP scanning is useful because of the way that it identifies, quantifies and extrapolates data from your environment.
It will help you to identify what belongs on your network and what does not and is very helpful during stock takes and site audits. It is not always possible to find the serial numbers of each and every component on your network so having a utility that will gather this information for you is very helpful.
Other features that the OpUtils SNMP tool offers is the ability to check the availability and route health of individual systems on your network. It uses a combination of SNMP and ICMP. The tool also shows a graph that helps with determining historical performance, as well as entire IP ranges and statuses of multiple targets.
The SNMP ping utility helps to check that the nodes in question that you are trying to investigate are SNMP capable, and then discover the basic information that you would need to fault find including the target’s DNS name, system name, location, system type, and system description.
After the SNMP discovery has completed then you can dig deeper with additional SNMP tools such as SNMP walker and SNMP Graph.
Pros:
- Offers a suite of tools that provide WoL, IP address management, and physical switch port mapping
- Gathers hostname, device status, and MAC address alongside IP address scans
- Identifies new machines via autodiscovery, great for large networks and continuous monitoring
- Available for both Windows server and nix operating systems
- Free version is great for smaller networks
Cons:
- ManageEngine is a large monitoring platform that offers a host of tools and features that may take time to fully explore
Overall this is a useful tool that is sure to come in handy during your day to day functions as a network engineer or technician, and the fact that it comes as a free version is especially useful. Start a 30-day free trial.
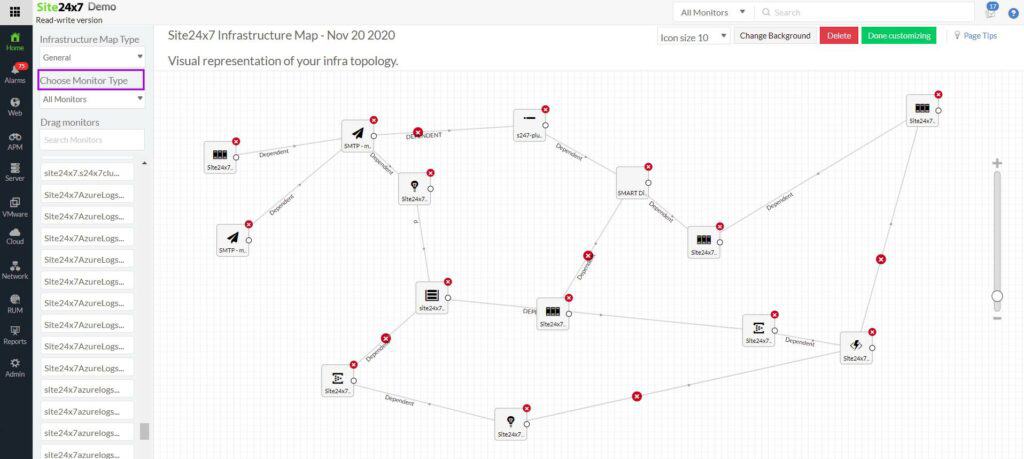
3. Site24x7 – FREE TRIAL
Site24x7 is an SNMP-based network device monitoring tool that provides real-time insights into the performance and health of network devices, including routers, switches, firewalls, and other SNMP-enabled hardware. By leveraging SNMP, Site24x7 can poll devices for performance data such as CPU usage, memory utilization, bandwidth, and interface status.
This protocol allows Site24x7 to automatically discover network devices and track their performance over time, providing administrators with valuable information about potential issues before they lead to downtime. With its ability to support SNMP v1, v2c, and v3, Site24x7 ensures secure, flexible, and efficient monitoring for a wide range of network infrastructure.
The package uses SNMP data to generate a hardware inventory and draw up a network topology map. As the SNMP polling repeats continuously, that system documentation gets updated automatically if any changes have occurred.
Site24x7’s SNMP-based monitoring is particularly useful for businesses that need to maintain network uptime and optimize performance. The platform provides customizable alerts and notifications that trigger when a device reaches a critical threshold, such as high CPU utilization or network interface errors. It will also interpret SNMP Traps into alerts.
These alerts help network administrators identify and resolve issues quickly, reducing the risk of network downtime.
The platform’s well-planned console allows administrators to set up and configure device monitoring with minimal effort. It also supports multi-site monitoring, making it ideal for businesses with large or distributed network infrastructures.
Pros:
- Automated network device monitoring
- Device and server availability checks
- Network inventory and topology map
- Ability to monitor multiple sites in a WAN
Cons:
- Doesn’t offer on-premises hosting options
You can investigate the SNMP functions of the Site24x7 platform by accessing a 30-day free trial.
4. SolarWinds SNMP Scanner
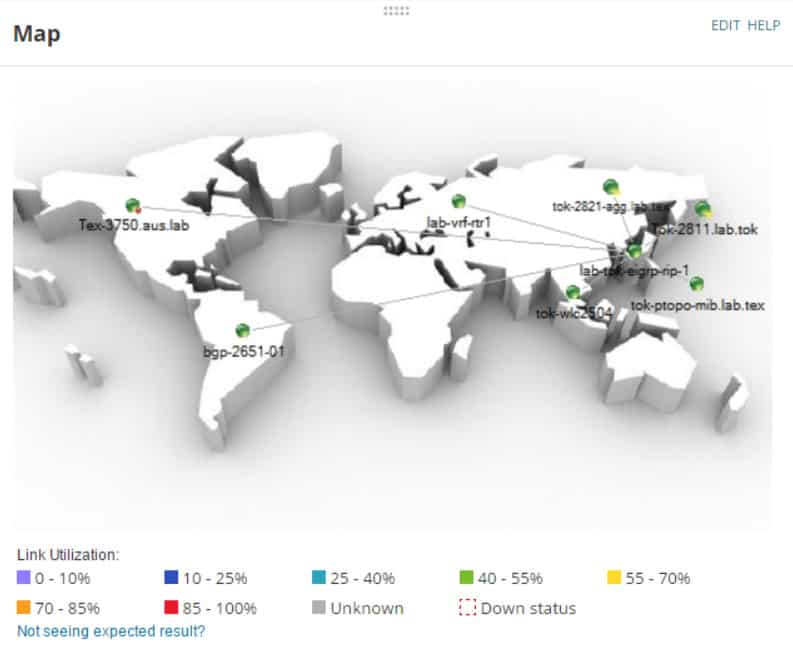
SolarWinds SNMP Scanner is a mapping tool that lets you discover and monitor everything on your network. It helps you discover network devices by performing SNMP sweeps and discovers and collects many detailed configuration reports about the entities on the network. Because of the way it scans and collects, it gives you the ability to map and create an overview of the current state of the network.
One of the great benefits of using this application is that it lets you monitor faults on the network, the availability of devices as well as the overall performance of the network. Performance metrics and MIBS data ensures that you have an accurate picture of the current state of network health and speed.
SolarWinds SNMP Scanner is especially useful in large and complex environments where there are devices from multiple vendors that you might not be able to monitor from traditional network scanning tools.
The mapping element means that you can easily detect and keep your environment up to date and labeled correctly. You can visualize in real-time whenever there are any errors on the map, as well as utilization stats for each of your links.
If a link goes down then you will know about it almost immediately with the Down Status indicator on your global map.
Overall this is a great tool that adds an additional layer of functionality to your network and will allow you to see any changes and faults as they come up within the environment.
Pros:
- Simple interface that scales well even on larger networks
- Provides a continuous live look into your network – recording address status
- Can run automated tests to alert sysadmin when devices come back online
- Highlights issues such as rogue DHCP servers and IP conflicts
- Consolidates IP, DHCP, and DNS information into a single view to help shorten troubleshooting time
Cons:
- The tool is designed for sysadmin, home users will likely not use all tools and features
Get started with a 30-day free trial.
5. Mitec Network Scanner
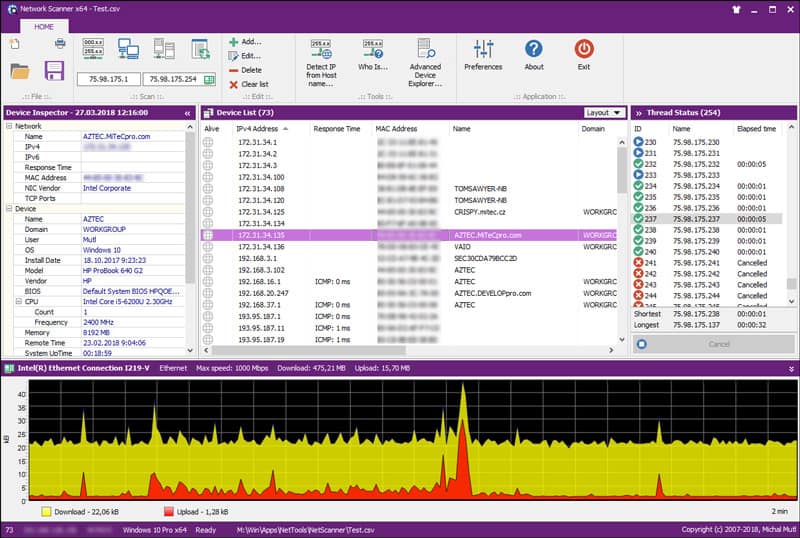
Mitec Network Scanner is a free and multi-threaded application that supports ICMP, Port, IP, NetBIOS, ActiveDirectory, and SNMP scanner with features that are advanced enough for IT professionals to use on a daily basis.
IT administrators, technicians, and even general users. There are standard features that are easy to use such as ping sweep, TCP and UDP scans, resource shares and services.
SNMP gives you all of the vital information about your network that you need to understand what is happening on the network in your organization. There are other great features such as a load and save results from previous scans, allowing you to generate and analyze trends on your network.
The application is available for free use and has many features that make it especially useful. It is Windows base and is capable of running on Windows XP, 2003, Vista, 7 Server2008, Server2008 R2, 8, 8.1, Server 2012, Server2012 R2, 10 and Server 2016.
It has the following features: ActiveDirectory, Network neighborhood, Ping (ICMP), IP Address, MAC Address (even across routers), MAC Vendor, Device name, Device domain/workgroup, Logged user, Operating system, BIOS, Model and CPU, System time and Up time, Device description, Type flags (SQL server, Domain controller etc.), Remote device date and time, TCP and UDP port scanning, SNMP services, Installed services on device, Shared resources, Sessions, Open Files, Running Processes, Terminal sessions, Event Log, Installed software, SAM account, WMI Queries, Powerful WhoIs client.
Pros:
- Does a great job at displaying ping metrics graphically and through verbose text
- Completely free tool
- Can run Whois lookups as well as DNS resolution on hostnames
- Great looking interface, easy to navigate even on larger networks
Cons:
- Would like to see more reporting options
Free to use privately – if you enjoy the application then you can donate here. It is free for personal and non-professional use.
6. Adrem Software SNMP Scanner
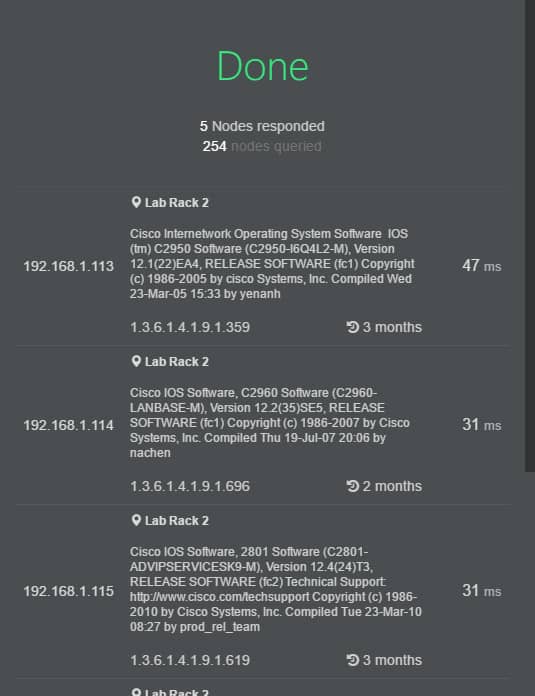
Adrem Software offers a free SNMP scanner from its Netcrunch Tools. Like most of the other free SNMP scanning tools that you are bound to encounter during your search for scanning utilities, Ardem Software’s SNMP Scanner is able to do quite a lot.
It can help you to pin point a single target PC on the network, or it can help you to reveal an entire subnet of computers.
Other free tools that they offer include ping, tracert, Wake on Lan, DNS info, Whois, DNS Audit, MAC Resolver, Subnet Calculator, Ping Scanner, Network Service Scanner and SNMP Scanner.
Pros:
- Part of a suite of WMI and troubleshooting tools
- Better suited for smaller environments
- Completely free
Cons:
- Not ideal for larger network environments
This software is free.
7. SNMP Device Network Management
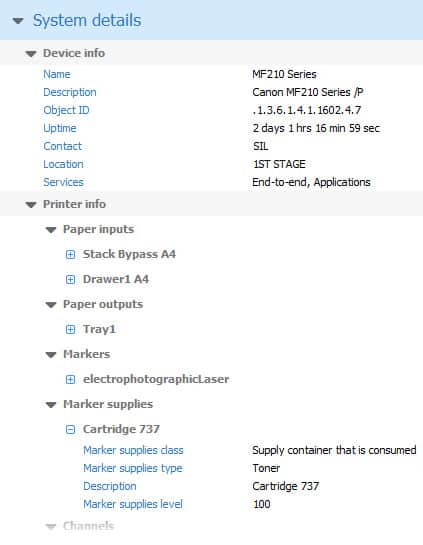
SNMP Device Network Management is a tool that will help you to maintain a full and detailed list of what IT related inventory you currently have connected to your network. It does all of this through SNMP scans, and can give you all of the information that you need to get the details of each and every SNMP enabled device in a relatively short space of time.
The best part about using SNMP is the fact that the process is agentless, meaning that you don’t have to go around to each individual computer and install a client application.
SNMP runs without needing anything installed to the computer, which makes the whole process much more streamlined for system administrators, especially when they are running inventory exercises on the network.
Pros:
- Can perform manual and automated SNMP sweeps across the network
- Simple user interface is easy to learn
- Provides a more streamlined approach to network management
- Very easy to install
Cons:
- Larger networks might require more advanced reporting and tools
The simplicity of this application makes it very easy for almost anyone to use, and while it is not free, it does offer users the chance to use it for 60 days.
Pricing starts at $90
8. NetScanTools SNMP – Core
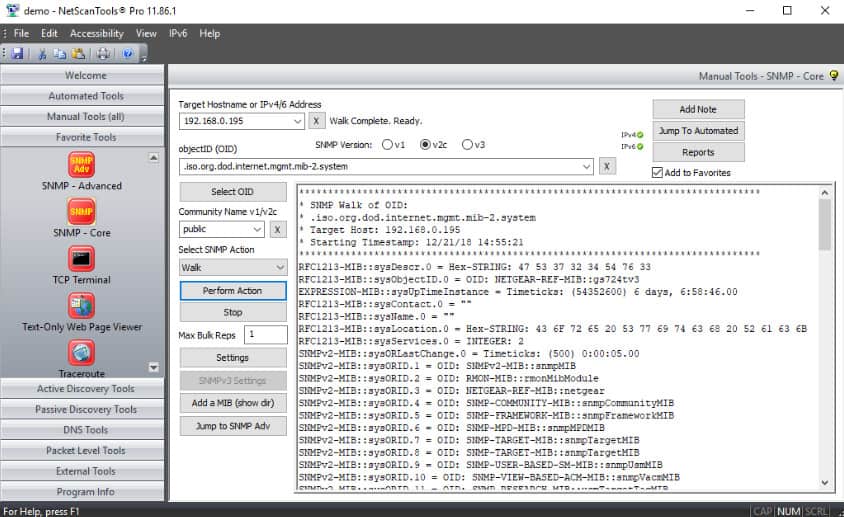
As we know by now, SNMP is one of the most powerful discovery tools that you can use on your network, allowing you to not only find all of the missing devices that have not been catalogued, but also device that have not been identified.
NetScanTools SNMP Core uses versions 1, 2c and 3 of SNMP, ensuring that regardless of the age of your SNMP equipped device that you are suitable compatible with them in the SNMP department.
Devices such as switches, printers and other appliances such as routers are mostly all SNMP compatible so you will have no problems trying to get the best out of your inventory attempts.
Pros:
- Offers a paid and free version, making it accessible for any budget
- Lightweight, the tool can be run on practically any endpoint
- Uses DNS queries to test name resolution and address scanning
Cons:
- The interface can feel outdated and a bit cluttered when scanning larger networks
- Only available for Windows operating systems
If you think that this application fits your requirements then you can download the demo from here. If you wish to purchase this application license then you can find the pricing and purchasing information right here. Pricing starts at $249
9. Secure Bytes SNMP Scanner
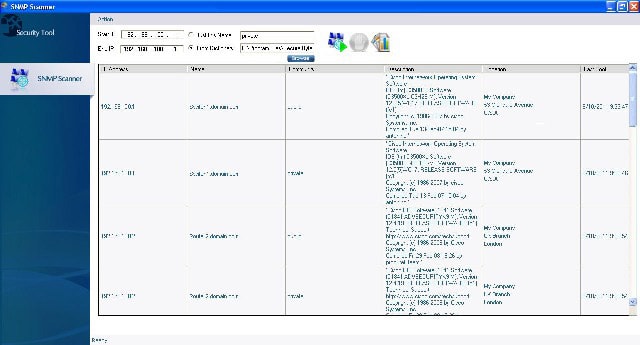
Our final contender on the list is none other than Secure Bytes SNMP Scanner. It is a commercial application that uses SNMP to map and track your network devices, giving you better visibility and management capabilities to catch your undocumented devices and hardware without having to go physically to each site and office.
This can make your workload significantly more manageable than having to do physical audits, so it is especially useful to those in an IT administrator role.
Pros:
- Lightweight scanner – great for smaller networks and one-off scans
- Allows you to map networks and identify devices automatically
- Provides simple visibility into devices on the network
Cons:
- The interface could use improvement
- Must contact sales for pricing
This application works really well in networked environments, and the trial can be downloaded directly below!
Contact Secure Bytes for pricing
SNMP Scanning Tools & Software FAQs
What are some popular SNMP scanning tools?
Some popular SNMP scanning tools include Nmap, OpenNMS, and Zenoss.
What are some benefits of using SNMP scanning tools?
Benefits of using SNMP scanning tools can include increased visibility into network devices, improved security by identifying vulnerabilities, and better asset management.
How does SNMP scanning work?
SNMP scanning works by using the SNMP protocol to retrieve information from network devices, including details on device configuration, performance, and status.
What are some common SNMP scanning metrics that organizations should track?
Common SNMP scanning metrics include network bandwidth usage, device uptime, and error rates.
What are some best practices for effective SNMP scanning?
Some best practices for effective SNMP scanning include regularly reviewing and updating monitoring policies, using automated tools to streamline monitoring processes, and analyzing historical data to identify trends and potential issues.
Related Post: Best IPAM Tools for IP Address Tracking Management