On October 6, 2015, close to Beijing, China, thousands of cars were stuck in one of the biggest traffic jams in history. It happened near a toll station on a 50-lane highway. Thousands of drivers were trapped for hours in an endless hair-pulling journey back home.
Fifty lanes merged into twenty lanes after a newly constructed toll, and it was also the end of an important National Holiday in China. Do you think a 50-lane highway is the fastest? Apparently not…
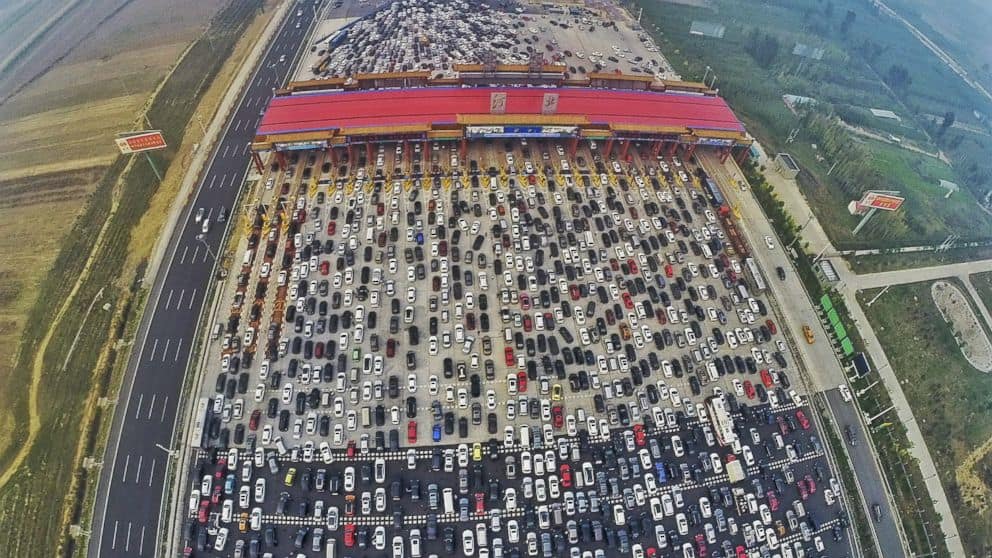

So why does this story relate to throughput? Imagine that the highway is a network connection and each car is a bit of data. The highway’s bandwidth was at its full capacity (before the toll and the holiday) and was able to handle millions of cars per hour.
In optimal conditions, cars would use all lanes and move at average speed. But in real life highways are busy. There are tolls, rush hour, roads under maintenance, accidents, and many more factors that affect how a car moves from point A to point B.
China’s highway probably had the best bandwidth in the world but the poorest throughput at that time. Concerning all these factors, the highway’s throughput was 1000 cars per hour.
What is Throughput exactly?
Throughput is the actual capacity of a system to send data to another, counting additional factors. In other words, it is the exact amount of data passing through the media from point A to point B in a determined amount of time.
When referring to communications, network throughput is the rate of message delivery over a single channel. Throughput shows its results as an average and uses “data units per time” metrics such as bits per second “bps” or packets per second “pps.”
Although the concept of throughput is similar to bandwidth, they are not the same.
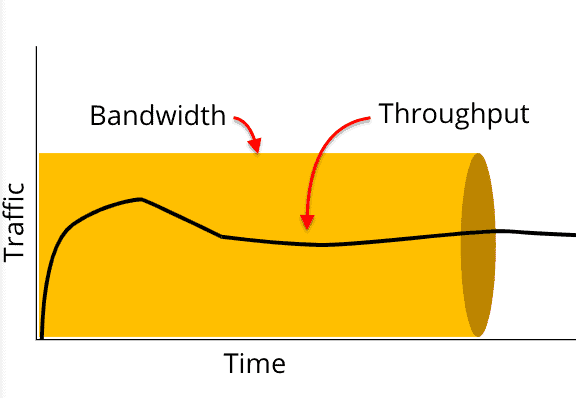
How is Bandwidth different than Throughput?
Bandwidth is the Total Capacity of a system to send data to another over a single media. It is like the size of the pipe or the highway, two lanes, three lanes, 50 lanes, etc. The concept relates to perfect and theoretical conditions.
But in real life, it is affected by countless factors, such as:
- Traffic load
- Packet loss
- Delay
- The hardware power
- Cabling
- Bit errors on the interface
- RF interference
- Encryption/Decryption
- CSMA/CA, and many more
When adding up all these factors, the bandwidth turns into a throughput. In common practices, the actual throughput should be at least 50% (or more) of the total bandwidth.
Throughput vs Connection Speed
Throughput is often confused with bandwidth and in worst cases with Internet Speed. When you buy an Internet connection at a certain speed, you are theoretically getting a specific bandwidth connection. But in real life, you’ll be affected by other factors and will end up getting the throughput.
Internet Speed is a general term, that refers to the amount of data transferred per second through a specific connection.
A good example is AT&T’s Internet Fiber connection offers. To get the 1000Mbps speed, the ISP will likely install powerful network devices, and optical cabling, and open up a wider bandwidth connection.
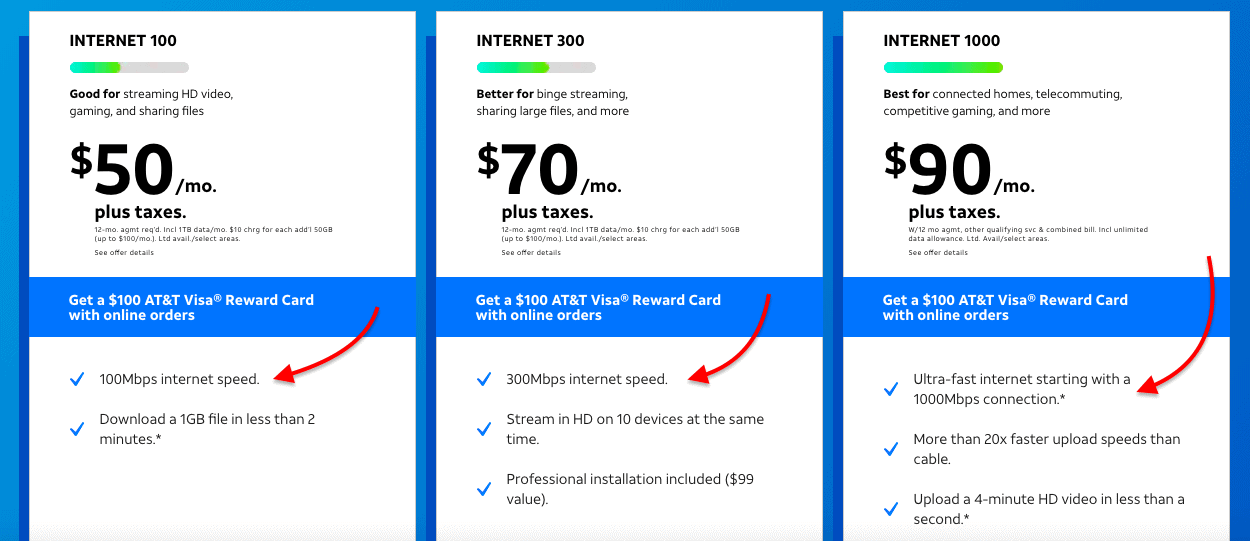
The concept of “Internet Connection Speed” is often used by marketers or sales representatives and is used by default to mean throughput, which is the actual rate of packet delivery over a specific medium.
In the following Speed Test performed in speedtest.net, the total connection speed (100Mbps) provided by AT&T was reduced to about 80%, which is not bad.
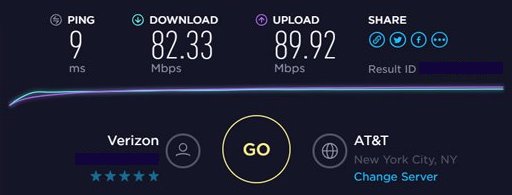
According to Speedtest from Ookla, the result of this test is an accurate measurement of HTTP throughput between the web server and the client. But speed test results such as this one will vary when you do the same test on different devices, at different times, and over various media. Not only the ISP will be a bottleneck, but also your infrastructure.
It is critical to measure network throughput with precision to guarantee that the SLA (Service-Level-Agreement) between provider or client is being met and also to make the network ready for any regulatory compliance.
The best Network Throughput Software and tools for Testing and measuring Bandwidth of 2025
Network administrators and Engineers use throughput as a metric to indicate the performance and health of a network connection. Instead of thinking in terms of bandwidth, they use throughput to see the real amount of bits or packets delivered from one network device to another.
What should you look for in a network throughput tester?
We reviewed the market for network throughput monitors and analyzed options based on the following criteria:
- A facility to run generated traffic through a network to stress test devices
- An option to test throughput over the network and also across the internet to a remote destination
- Systems to watch ongoing live activity
- Options to measure wireless networks as well as LANs
- Systems that can run tests automatically on a schedule to see changes in network performance
- A free trial to enable assessment before paying or a free tool
- Value for money from a comprehensive network monitor that offers a range of testing and monitoring services
With these selection criteria in mind, we looked for useful facilities that offer both ongoing monitoring of network throughput performance and also provide an on-demand testing utility. We made sure to include both free and paid systems.
Let’s take a look at a couple of tools used by professionals that can measure network throughput effectively.
Here is our list of the six best network throughput testers and monitors:
- SolarWinds Network Bandwidth Analyzer Pack This package includes a network device monitor plus network bandwidth analysis features, which provide all of the network monitoring services that you could possibly need. Runs on Windows Server.
- IxChariot This cloud-based service measures network utilization on LANS and on wireless networks and is particularly useful for testing network capacity through generated traffic.
- LAN Speed Test from TotuSoft This network performance monitor is useful for testing capacity and speed on specific actions, such as file transfers across wired and wireless networks. Runs on Windows, Windows Server, and macOS.
- Iperf3 This free testing system measures the maximum available bandwidth on a network through tests with a range of adjustments to network settings and enables tests to carry on over the internet to remote test servers. Available for Windows, macOS, Linux, Unix, Android, iOS.
- TamoSoft Throughput Test This free utility will measure throughput speed on test transmissions along with other metrics, such as packet loss and jitter. Available for Windows, Windows, Server, macOS, Android, and iOS.
- NetStress This free tool tests the performance of wireless networks with generated traffic and reports on a range of metrics including throughput speed and capacity. Runs on Windows.
1. SolarWinds Network Bandwidth Analyzer Pack
The Network Bandwidth Analyzer Pack from SolarWinds is an advanced bandwidth analyzer. This pack is an add-on to two popular SolarWinds software, Network Performance Monitor “NPM” and the SolarWinds NetFlow Traffic Analyzer “NTA”.
Unique Feature
Leverages AI, supports multiple vendors, generates dependency maps, and more.
Why do we recommend it?
Makes it easy to detect, diagnose, and resolve network issues through bandwidth analysis. Plus, it combines this analysis with data from your entire infrastructure for comprehensive insights.
This tool is not only capable of measuring throughput, but it can also find the root causes of a slow network. It accomplishes this, by identifying network faults, monitoring Network and server availability, and tracking the performance of devices across the flow of data.
The SolarWinds Bandwidth Analyzer Pack allows you to find, diagnose, and solve network, bandwidth, and traffic performance issues that might be causing your low throughput.
When the network is too slow, you can use this tool as a throughput monitor (with the help of NetFlow, sFlow, and other protocols) to find users or applications that are consuming your precious bandwidth.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for network administrators of large organizations who want to fix network issues.
Pros:
- Supports multiple protocols like NetFlow, great for monitoring Cisco equipment
- Both tools work well alongside each other to help view traffic patterns and bandwidth usage
- Easy-to-use interface automatically highlights bandwidth hogs and other network traffic outliers
- Scales well, designed for large enterprise networks
- Can view traffic on a per-hop basis, allowing for granular traffic analysis
Cons:
- Built for enterprise use, not designed for small home networks
The SolarWinds Bandwidth Analyzer Pack is designed to be compatible exclusively with Windows Server versions 2008 R2 SP1, 2012, 2012 R2, and 2016. It offers a 30-day free trial, allowing users to download and experience a fully functional version at no cost for a duration of 30 days.
2. IxChariot
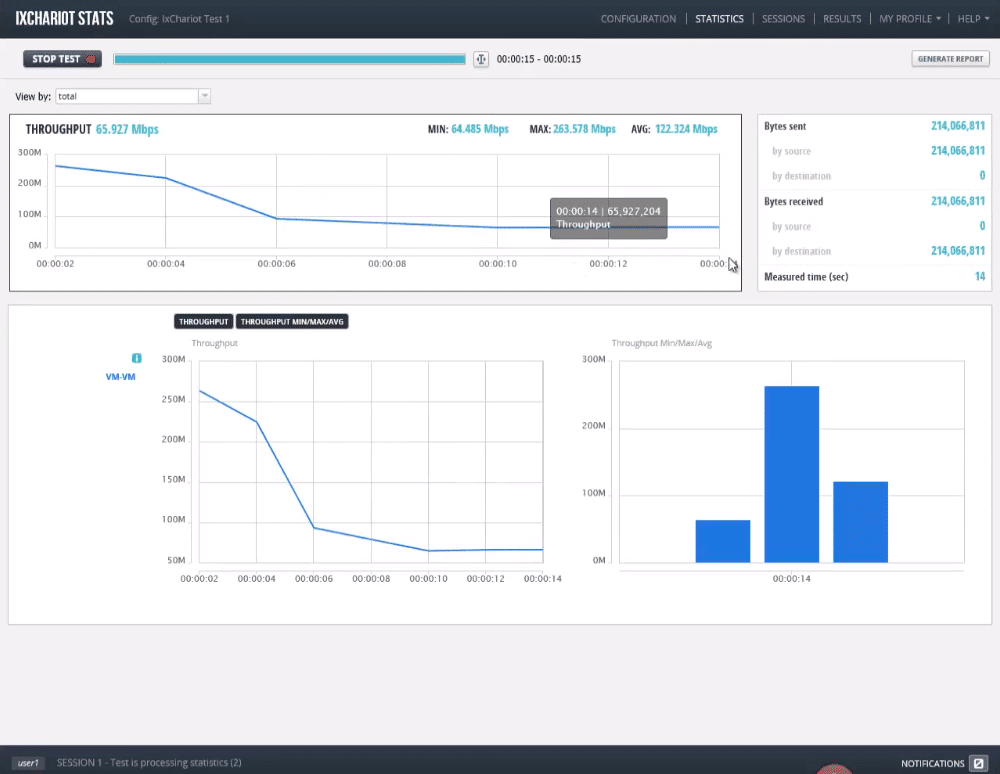
IxChariot is a product developed by Ixia, which is a side business of the Keysight Technologies group. IxChariot is a comprehensive performance monitoring and analysis software. It is aimed at enterprise-size networks and can scale up to 10,000 connections that represent hundreds of thousands of end-users.
Why do we recommend it?
Simulates application traffic based on your traffic patterns to help you understand the key patterns and performance metrics.
The software is one of the best for monitoring Wireless LAN and VoIP traffic. It gives rich details and graphics. This product not only keeps track of your throughput but also of other key performance metrics such as packet loss, jitter, delay, MOS, and OTT video analytics.
IxChariot uses throughput as one of the primary data points for testing and gathering information. For example in WiFi monitoring, the wireless standard 802.11 and the distance to the Base Station “BS” will influence throughput and response time. If throughput changes over time, IxChariot can monitor signal strength.
IxChariot can evaluate:
- Peak TCP Throughput:
The maximum network throughput of the network. - Peak UDP Throughput:
It is an indicator of basic network performance.
You can run the performance endpoints on a variety of environments all from a central platform, such as PCs, mobiles, VMs, to cloud deployments.
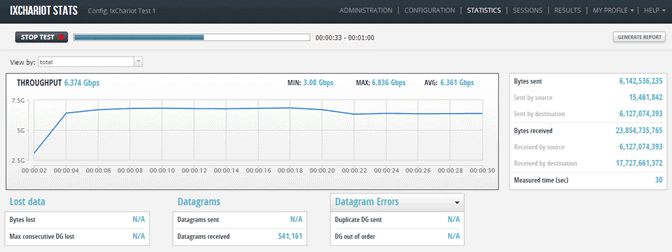
Who is it recommended for?
A good choice for network assessment, network performance monitoring, and for troubleshooting networks.
Pros:
- Highly scalable cloud-based monitor
- Simple and intuitive graphics and reporting
- Best suited for enterprise users
- Includes wireless monitoring
Cons:
- Not ideal for smaller organizations
This product is compatible with older Windows operating systems, including XP, 2000, ME, and NT4 (SP3 and above), requiring minimal hardware specifications such as a Pentium 300 processor, 64 MB of Memory, and 23 MB of Disk Space. To know the total cost, interested buyers need to request a formal quote. Additionally, a free online demo is available by registering on the ixChariot website.
3. LAN Speed Test from TotuSoft
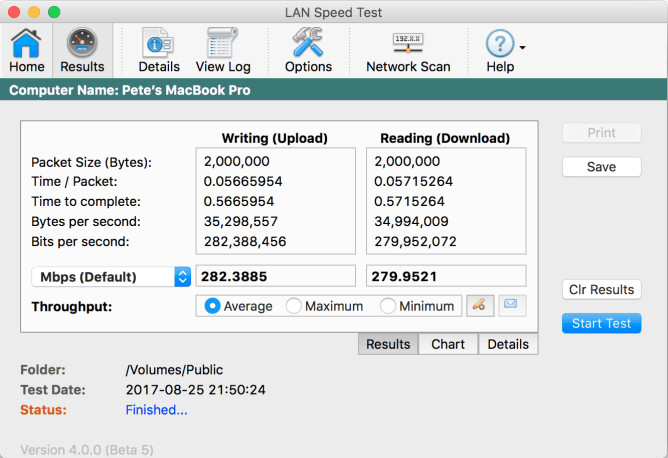
LANSpeed Test is a speed evaluation software developed by TotuSoft. It is a simple tool capable of measuring file transfers, drives, and LAN speeds, either on wired or wireless networks. The tool is easy to use and highly portable. No installation is required.
Why do we recommend it?
A simple, yet powerful tool to measure file transfer, wired and wireless LAN speeds, hard drive capacity, and other factors that can affect network performance.
LAN Speed Test is capable of evaluating the speeds of LANs by testing shared folder transfer. It can also check the speed of USB drives and hard drives. You can transfer up to 1000 packets and files of 9 GB in size, and the tool will still perform all calculations smoothly.
When testing the speed, the tool is capable of showing the results on average, maximum, and minimum throughput.
To start testing network speed with this tool, choose a folder or file and begin to transfer it. Lan Speed Test will create a file in the memory, move it without caching, keep track of time, and perform all necessary speed calculations.
This tool is compatible with LST Server (LAN Speed Test Server) for network performance results, and despite the name, it is also capable of testing WAN Internet speeds.
Who is it recommended for?
Works mostly for home-based small networks.
Pros:
- Simple lightweight tools
- Can check drive speed as well as network metrics
- Can test with traffic as large as 9GB packets
- Easily displays minimum, maxim, and average throughput
Cons:
- Could use more visual data features
This product is compatible with Windows 7, Windows Server 2008, or later versions, as well as with Mac OS 10.7.5 (Lion) or later. The pricing varies based on the license type: $10.00 per user for the Full License (Single), $45.00 for the “5 pack” license, $85.00 for the “10 Pack” license, and $150.00 for the unlimited license. A Free LAN Speed Test Server with limited features is available for download, enabling you to start testing your throughput immediately.
4. Iperf3
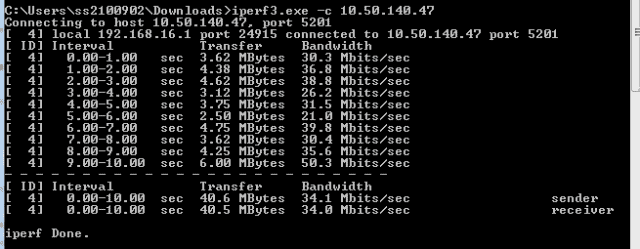
Iperf3 is a free and open-source command line tool for measuring network bandwidth & throughput in real-time. It is based on the Iperf series software that performs active measurements to find the maximum attainable bandwidth.
Why do we recommend it?
Iperf3 is a cross-platform tool that can come in handy for assessing and tuning your network performance. It supports the running of parameters associated with tuning, timing, buffering, and more.
The Iperf3 can test the maximum bandwidth and throughput in IPv4 or IPv6 networks. As we learned before, to improve overall network performance, we need to enhance throughput and reduce latency. Iperf3 allows you to perform tests and to produce statistics so that you can tune up the TCP or UDP connections in a particular flow.
Fortunately, the Iperf3 allows you to adjust the testing parameters like timing, buffers, or protocols (TCP, UDP, SCTP). As a result, the tool can report insightful information such as:
- Max/Min Bandwidth (Transfer Rate)
- Max/Min Throughput
- Packet loss
- Delay
- Jitter
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is well-suited for organizations that run remote backups or want to synchronize databases across multiple instances.
Pros:
- Free, open-source tool
- Cross-platform compatibility gives it extended usability on MacOS and FreeBSD
- Very lightweight, can run efficiently on resource-limited machines
Cons:
- Must be installed on both the endpoint and the monitoring machine
- Designed for technical users, not as user-friendly as most tools
IPerf is a versatile, cross-platform tool compatible with a wide range of operating systems including Windows, Linux, Android, MacOS X, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, VxWorks, and Solaris. As a free and open-source application, iperf3 can be easily downloaded at no cost from its official site, making it accessible to a variety of users.
5. TamoSoft Throughput Test
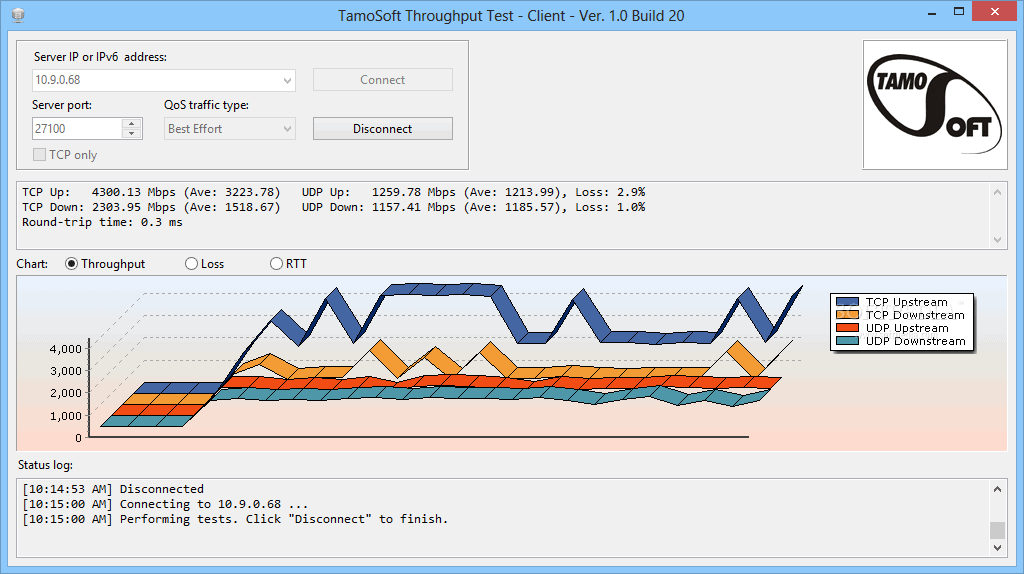
TamoSoft Throughput Test is a simple yet powerful throughput testing tool. It is a 100% free utility capable of measuring the throughput of either UDP and TCP data streams. TamoSoft can calculate and report upstream or downstream throughput statistics, packet loss, and Round-Trip-Time “RTT.” The tool shows the results both in numeric form and in graphics.
Key Features:
- It supports both IPv4 and IPv6
- Modify port, either UDP or TCP
- Evaluate performance based on QoS traffic type
- Displays a status log
Why do we recommend it?
This is a small utility to test the performance of a Wi-Fi network. It continuously sends streams of UDP and TCP data and calculates the important metrics.
TamoSoft uses a client/server application approach to measure the connection. The Server listens for connections, the client and server exchange information and the client calculates and sends the final metrics.
Who is it recommended for?
A good choice for home-based and small business networks that want to test the performance of their wired and wireless connections.
Pros:
- Simple data visualization – but it gets the job done
- Lightweight tool
- Can test traffic across different VLANs and QoS settings
- Supports Android, MacOS, Windows, and iOS environments
Cons:
- Can take time to fully explore the tool
The TamoSoft Throughput Test, a freeware, is supported across multiple platforms including Windows, MacOS, Android, and iOS. You can download the Throughput test directly from the TamoSoft official site, offering wide accessibility for various users.
6. NetStress
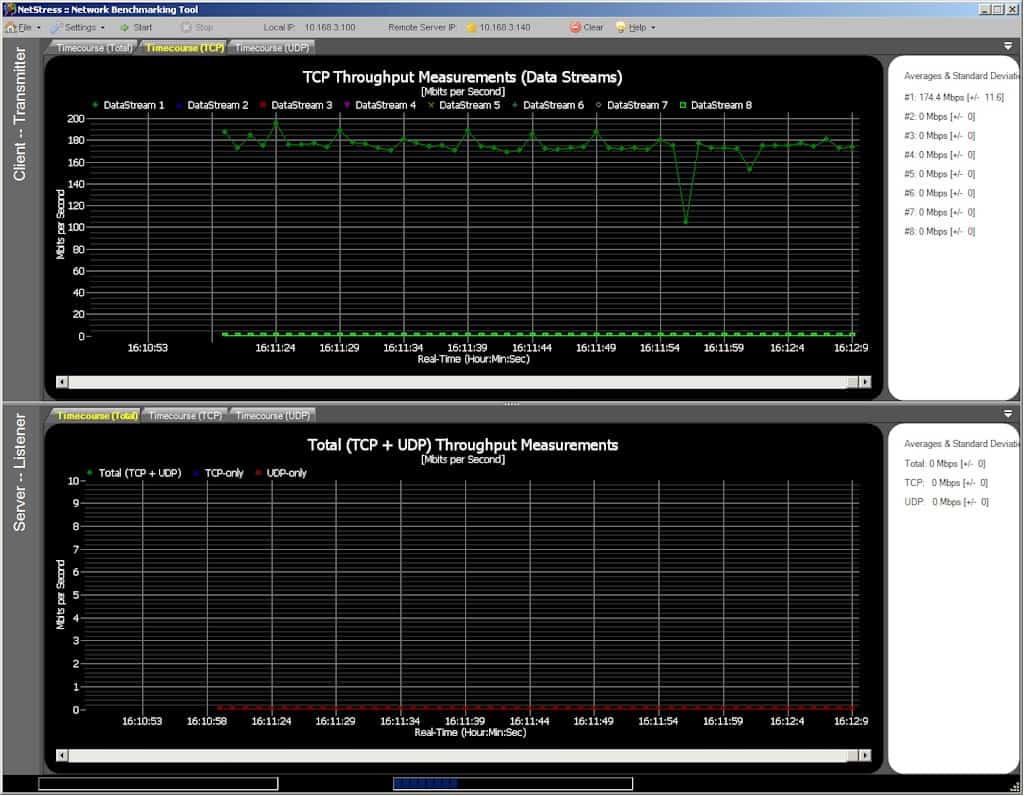
NetStress is a free throughput testing tool for UDP and TCP connections, developed by Nuts about Nets. It specializes in measuring throughput for 802.11(Wi-Fi) networks but can work on wired networks. Although NetStress is a Client/Server-based tool, you can also use it as a single instance. NetStress can produce real-time graphics of your network’s throughput.
Although you can run TCP or UDP streams simultaneously, you can only do upstream or downstream tests separately. NetStress just run tests on IPv4 networks.
Key Features:
- It can be installed as a single instance. (Server or Server/Client)
- It supports up to eight TCP and UDP data streams
- Auto-discovers hosts
- Modify TCP/UDP segment size
- Set data flow direction, display units, and MTU
- It displays results in KBps, Kbps, MBps, or Mbps
- It shows the packet transmission rate
Why do we recommend it?
A simple tool that sends bulk data using TCP and UDP protocols, and calculates the throughput of your ethernet device or network. It can also be extended for path analysis.
NetStress uses a performance benchmark to test the network and track changes. This benchmark is defined when the network is running smoothly. Later it is used as a reference to compare when the network’s performance is declining.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for small networks.
Pros:
- Simple graphical network analyzer
- Can view TCP and UDP streams at once
- Highly detailed reporting
Cons:
- More of a technical tool – not for non-technical users
NetStress is exclusively compatible with Windows systems and is available at no cost, being 100% free. You can download NetStress from its official website, making it an accessible tool for users on Windows platforms.
Conclusions
Now that you understand throughput, you know that the time it takes for bits going from point A to point B will depend on many factors. Just like the cars running in a five-lane highway towards a destination, they will have delays, tolls, accidents, etc.
The width of the highway (bandwidth) can provide a total rate but does not give you the actual rate. When referring to communications, network throughput is the actual rate of messages successfully delivered over a single channel.
The problem is that throughput is often confused with bandwidth and even worst with Internet Speed. When you buy an Internet connection at a certain speed, you are theoretically paying for a specific bandwidth connection.
But in real life, you’ll be affected by other factors and will ultimately get a throughput. But no problem, you can still optimize it. The idea of throughput optimization is to bring it up as close as possible to the total bandwidth.
A high ratio of successful message delivery will cause a high throughput which will ultimately improve performance and the network’s capacity. Some of the tools listed above will help you measure and create benchmarks.
Some others will go beyond and even help you optimize it. Measuring as soon as possible is the best way to create a reference point, and use it for comparison later. Start testing it today!
Network Throughput FAQs
What are some common tools for measuring network throughput?
Some common tools for measuring network throughput include:
- Iperf, a command-line tool that can generate TCP and UDP traffic to measure network throughput and latency.
- PingPlotter, a network diagnostic tool that provides real-time monitoring and alerts for network performance issues.
- SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, a network monitoring and analysis tool that provides detailed information about network performance and usage.
How can I accurately measure network throughput?
To accurately measure network throughput, you should:
- Use a tool that can generate realistic network traffic patterns and measure both upstream and downstream throughput.
- Conduct tests under normal network operating conditions to capture realistic network usage patterns.
- Use multiple test points and take the average to account for variability in network performance.
- Minimize interference from other network traffic or devices during the test.
- Conduct tests over extended periods of time to capture variations in network usage.
How can I troubleshoot issues when measuring network throughput?
To troubleshoot issues when measuring network throughput, you can try the following: Check the configuration settings for your testing tool to make sure they are correct. Verify that your network configurations and settings are correct and up-to-date. Check for any error messages or warnings that may indicate a problem with the testing tool or network configuration. Try adjusting testing parameters or configurations to see if this improves performance or accuracy.